Issues With Aortic Valve Calcification: Understanding The ICD-10 Code
What is Aortic Valve Calcification ICD 10?
Aortic valve calcification is a condition in which calcium deposits build up on the aortic valve, causing it to become stiff and narrow. This can restrict blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, leading to serious health problems. In ICD-10, the code used to classify this condition is I06.2.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for aortic valve calcification is I06.2. This code falls under the larger category of rheumatic aortic valve diseases, which includes a variety of conditions affecting the aortic valve. By using this specific code, healthcare providers can accurately document and track cases of aortic valve calcification.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
In terms of Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG), cases of aortic valve calcification are typically grouped under DRG 251 – Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures with Acute Myocardial Infarction. This DRG includes procedures related to the treatment of heart conditions, including those affecting the aortic valve.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
For those still using the ICD-9 coding system, the equivalent code for aortic valve calcification is 424.1. This code falls under the broader category of aortic valve disorders and is used to classify cases of aortic valve calcification in a similar manner to ICD-10.
Code History
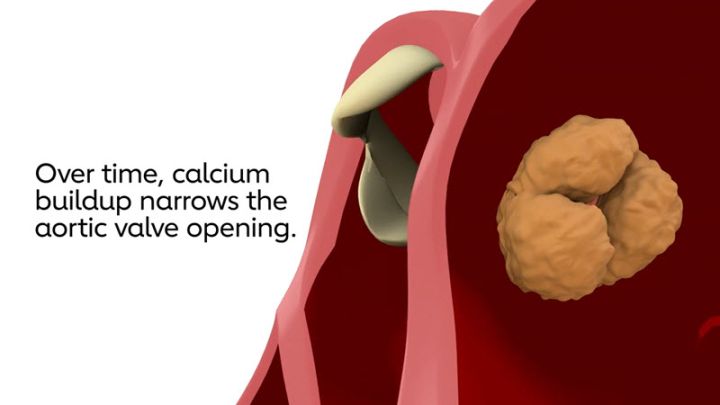
The ICD-10 code I06.2 for aortic valve calcification was first introduced in 1996 as part of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Since then, it has been used by healthcare providers and researchers to accurately document and track cases of this condition.
Approximate Synonyms
Some other terms that may be used interchangeably with aortic valve calcification include aortic valve sclerosis, aortic stenosis, and calcific aortic valve disease. While these terms may vary slightly in their clinical definitions, they all refer to the presence of calcium deposits on the aortic valve.
Clinical Information
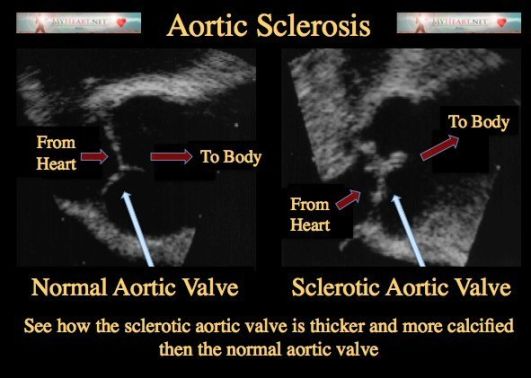
Aortic valve calcification is a progressive condition that typically occurs as a result of aging or underlying heart disease. As calcium deposits accumulate on the aortic valve leaflets, they can cause the valve to become stiff and narrowed, leading to decreased blood flow and potential complications.
Causes
The exact cause of aortic valve calcification is not fully understood, but it is believed to be linked to a combination of factors, including age, genetics, and lifestyle choices. Certain medical conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, may also increase the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms

In the early stages, aortic valve calcification may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness. In severe cases, aortic valve calcification can lead to heart failure or other complications.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing aortic valve calcification typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and cardiac catheterization to assess the extent of calcification and determine the best treatment approach.
Treatment
The treatment options for aortic valve calcification depend on the severity of the condition and the presence of symptoms. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, may be sufficient to manage symptoms. More severe cases may require medication, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery to repair or replace the aortic valve.
Conclusion
Aortic valve calcification is a serious condition that can have significant implications for heart health. By accurately documenting and coding cases of aortic valve calcification using the ICD-10 code I06.2, healthcare providers can ensure proper diagnosis and treatment for affected individuals.
FAQs
1. Can aortic valve calcification be prevented?
2. What are the risk factors for developing aortic valve calcification?
3. How is aortic valve calcification diagnosed?
4. What are the treatment options for aortic valve calcification?
5. Is aortic valve calcification a common condition?