Decoding ADHD: Understanding ICD-10 Codes For Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
What is ADHD?
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can interfere with daily functioning and social interactions.
Code Information

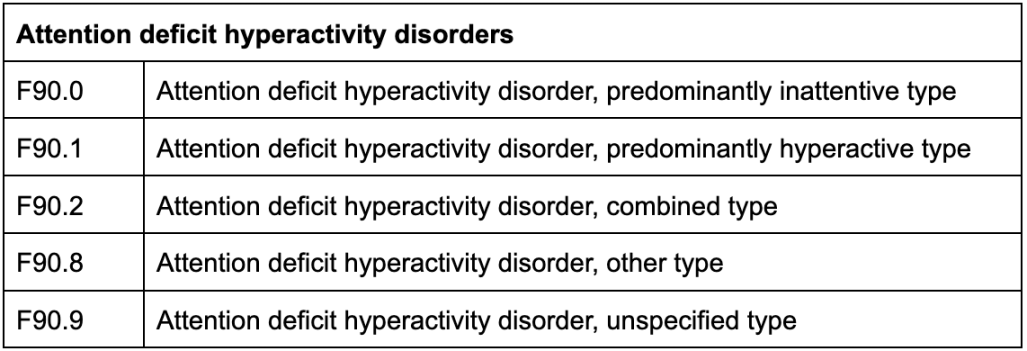
The ICD-10 code for ADHD is F90. It falls under the category of mental, behavioral, and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
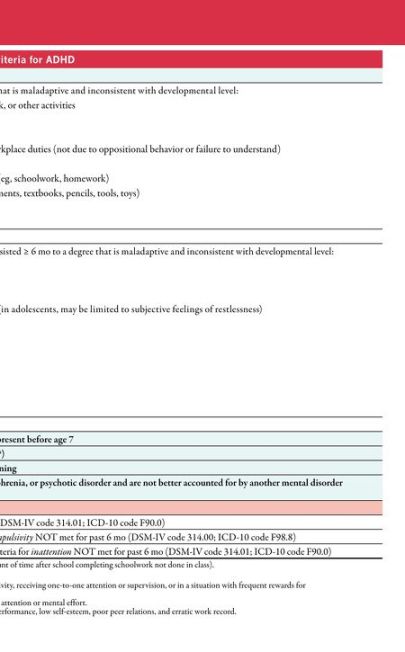
ADHD does not have a specific MS-DRG as it is typically managed on an outpatient basis.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The equivalent ICD-9 code for ADHD is 314.01.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for ADHD was introduced in 2015 as part of the updated coding system.
Approximate Synonyms
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
ADHD, predominantly inattentive type
ADHD, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type
Clinical Information
ADHD is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. It is commonly diagnosed in childhood but can persist into adulthood.
Causes
The exact cause of ADHD is not known, but research suggests that genetics, brain chemistry, and environmental factors play a role in its development. Certain risk factors, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and exposure to toxins during pregnancy, may increase the likelihood of developing ADHD.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ADHD vary depending on the individual but can include difficulty concentrating, impulsivity, hyperactivity, and forgetfulness. Children with ADHD may have trouble following instructions, staying organized, and completing tasks.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ADHD is typically based on a comprehensive evaluation that includes a physical exam, medical history, and assessment of symptoms. Healthcare providers may use standardized rating scales, questionnaires, and behavioral observations to help make a diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for ADHD often involves a combination of medication, therapy, and behavioral interventions. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamine salts, are commonly used to help manage symptoms. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and parent training, can also be effective in teaching coping strategies and improving social skills.
Conclusion
ADHD is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that can have a significant impact on daily life. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and thrive in school, work, and social settings.
FAQs
1. Can adults be diagnosed with ADHD?
2. Is ADHD a lifelong condition?
3. Are there natural remedies for managing ADHD symptoms?
4. How does ADHD affect academic performance?
5. Can ADHD be cured?