Dilatation Of Aortic Root: Coding Challenges With ICD-10
What is Dilatation Aortic Root ICD 10?
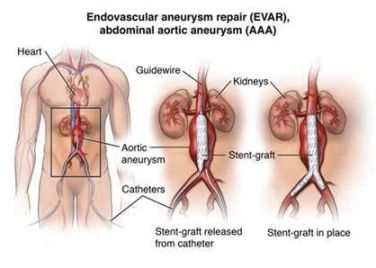
Dilatation aortic root ICD 10 refers to the enlargement or widening of the aortic root, which is the section of the aorta that is closest to the heart. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, high blood pressure, and connective tissue disorders.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for dilatation aortic root is I71.01.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
The MS-DRG for dilatation aortic root is MS-DRG 297 – Cardiac Arrhythmia and Conduction Disorders with MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The ICD-9 code for dilatation aortic root is 441.01.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for dilatation aortic root was first introduced in 2016.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that are used interchangeably with dilatation aortic root include aortic root aneurysm and aortic root enlargement.
Clinical Information
Dilatation of the aortic root can lead to serious complications, such as aortic dissection or rupture, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing this condition.
Causes
The exact cause of dilatation aortic root is not always known, but it is believed to be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Conditions such as Marfan syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, and a family history of aortic aneurysms can increase the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms
Many individuals with dilatation aortic root may not experience any symptoms initially. However, as the condition progresses, some common symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of dilatation aortic root typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as echocardiography, CT scan, or MRI. Blood tests may also be performed to rule out any underlying conditions.
Treatment
Treatment for dilatation aortic root may vary depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, medication to control blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications may be prescribed. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the dilated aortic root.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dilatation aortic root is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have this condition, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
FAQs
1. Can dilatation aortic root be prevented? While genetic factors may play a role in the development of this condition, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors such as high blood pressure can help reduce the risk of dilatation aortic root.
2. Is dilatation aortic root a common condition? Dilatation aortic root is relatively rare, but it can occur in individuals with certain genetic predispositions or underlying health conditions.
3. How is dilatation aortic root treated? Treatment for dilatation aortic root may include medication to manage symptoms and prevent complications, or surgery to repair or replace the dilated aortic root.
4. What are the long-term effects of dilatation aortic root? If left untreated, dilatation aortic root can lead to serious complications such as aortic dissection or rupture, which can be life-threatening.
5. Can dilatation aortic root be diagnosed with a routine physical exam? While a routine physical exam may detect certain signs of dilatation aortic root, a definitive diagnosis typically requires imaging tests such as echocardiography or CT scan.