A Quick Guide To ICD-10 Code For Aortic Stenosis: I35.0
What is Aortic Stenosis?
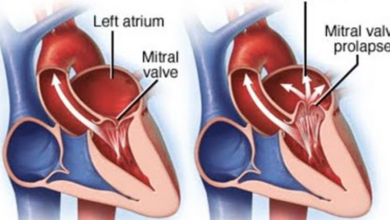
Aortic stenosis is a condition in which the aortic valve in the heart narrows, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood effectively. This can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. It is a common condition, especially in older adults, and if left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as heart failure.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for aortic stenosis is I35.0. This code is used to classify the condition in medical records and is essential for billing and insurance purposes. It is important to use the correct code to ensure accurate documentation of the patient’s condition and to facilitate proper treatment and care.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

For aortic stenosis, the MS-DRG code is 222. This code is used to group patients with similar diagnoses and treatment patterns for reimbursement purposes. It helps hospitals and healthcare providers determine the appropriate level of care for patients with aortic stenosis and ensures that they are reimbursed correctly for their services.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The ICD-9 code for aortic stenosis is 394.0. This code was used before the transition to ICD-10 and is no longer valid for billing and documentation purposes. It is important for healthcare providers to use the current ICD-10 code I35.0 for accurate coding and classification of aortic stenosis.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for aortic stenosis was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10. It was created to provide a more specific and detailed classification of diseases and conditions, including aortic stenosis. The code has since been updated and revised to ensure accuracy and relevance in medical coding practices.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for aortic stenosis include aortic valve stenosis, aortic valve sclerosis, and aortic valve calcification. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the narrowing of the aortic valve that occurs in aortic stenosis. Healthcare providers may use these synonyms in medical records and documentation to accurately describe the patient’s condition.
Clinical Information
Aortic stenosis is typically caused by the buildup of calcium deposits on the aortic valve, which restricts blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body. This can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Diagnosis of aortic stenosis is usually made through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and cardiac catheterization.
Causes
The exact cause of aortic stenosis is not always clear, but it is often associated with age-related changes in the heart valve. Other risk factors for developing aortic stenosis include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a history of heart disease. In some cases, aortic stenosis may be present at birth due to a congenital heart defect.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of aortic stenosis include chest pain or tightness, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and fainting. These symptoms may worsen over time as the condition progresses and the aortic valve becomes more narrowed. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as aortic stenosis can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of aortic stenosis typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests such as echocardiography, and cardiac catheterization to assess the severity of the condition. Blood tests may also be performed to check for markers of heart disease. A healthcare provider will use this information to determine the best course of treatment for aortic stenosis.
Treatment
Treatment for aortic stenosis may include medications to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the condition, as well as surgical procedures such as aortic valve replacement or repair. The appropriate treatment plan will depend on the severity of the aortic stenosis and the patient’s overall health. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment options for your individual case.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aortic stenosis is a common heart condition that can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential