Implications Of Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma In ICD-10 Coding
What is Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma?
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma, also known as invasive ductal carcinoma, is the most common type of breast cancer. It starts in the milk ducts of the breast and then invades the surrounding breast tissue. This type of breast cancer accounts for about 80% of all breast cancer diagnoses.
Code Information
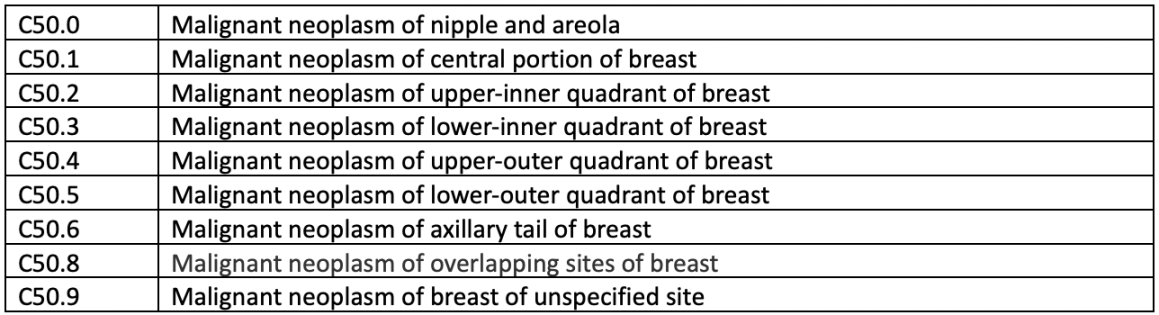
The ICD-10 code for infiltrating ductal carcinoma is C50.9. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses and procedures for billing and statistical purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

The MS-DRG for infiltrating ductal carcinoma is MS-DRG 821 – Lymphoma and Leukemia with Major O.R. Procedure with MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for infiltrating ductal carcinoma is 174.9 – Malignant neoplasm of breast, unspecified site.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for infiltrating ductal carcinoma was implemented in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used interchangeably with infiltrating ductal carcinoma include invasive ductal carcinoma and breast adenocarcinoma.
Clinical Information
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma is characterized by the cancer cells forming a solid mass or lump in the breast tissue. These cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
Causes
The exact cause of infiltrating ductal carcinoma is unknown, but risk factors may include genetic mutations, hormonal factors, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and alcohol consumption.
Symptoms
Symptoms of infiltrating ductal carcinoma may include a lump or thickening in the breast, changes in the size or shape of the breast, nipple discharge, or skin changes such as redness or dimpling.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of infiltrating ductal carcinoma is typically confirmed through a combination of imaging tests, such as mammograms and ultrasounds, and a biopsy of the breast tissue.
Treatment
Treatment for infiltrating ductal carcinoma may involve a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. The specific treatment plan will depend on the stage of the cancer and other individual factors.
Conclusion
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma is a common type of breast cancer that starts in the milk ducts of the breast and can invade surrounding tissue. Early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes for patients with this type of cancer.
FAQs
Q: What is the prognosis for infiltrating ductal carcinoma?
A: The prognosis for infiltrating ductal carcinoma depends on the stage of the cancer at diagnosis and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Q: Are there any risk factors for infiltrating ductal carcinoma?
A: Risk factors for infiltrating ductal carcinoma may include genetic mutations, hormonal factors, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and alcohol consumption.
Q: How is infiltrating ductal carcinoma treated?
A: Treatment for infiltrating ductal carcinoma may involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
Q: Can infiltrating ductal carcinoma spread to other parts of the body?
A: Yes, infiltrating ductal carcinoma can spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
Q: Is infiltrating ductal carcinoma hereditary?
A: While genetic mutations may increase the risk of infiltrating ductal carcinoma, the majority of cases are not hereditary.