Decoding Cholangiocarcinoma: Understanding ICD-10 Codes For Bile Duct Cancer
Cholangiocarcinoma ICD 10 Code
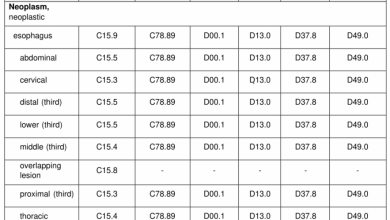
Cholangiocarcinoma is a type of cancer that affects the bile ducts, which are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. In ICD-10, cholangiocarcinoma is classified under the code C22.1.
ICD-10 Code Information
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is a system used by healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States. Cholangiocarcinoma falls under the category of malignant neoplasm of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts, specifically code C22.1.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
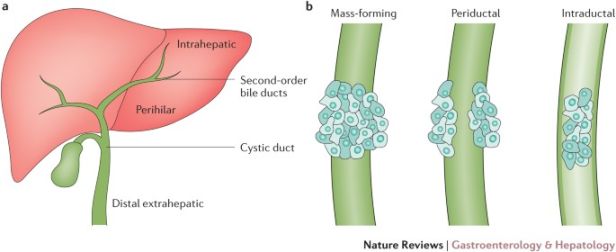
In terms of Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups (MS-DRG), cholangiocarcinoma falls under DRG 435, which is titled Malignancy of Hepatobiliary System or Pancreas with MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
If you need to convert the ICD-10 code for cholangiocarcinoma to an ICD-9 code, the corresponding code is 155.1.
Code History
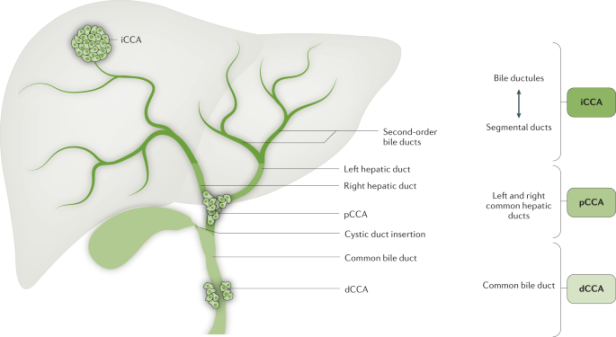
In the previous version of the ICD coding system (ICD-9), cholangiocarcinoma was classified under the code 155.1, which is the same as the ICD-9 code for this condition.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for cholangiocarcinoma include bile duct cancer, intrahepatic bile duct cancer, and bile duct adenocarcinoma.
Clinical Information
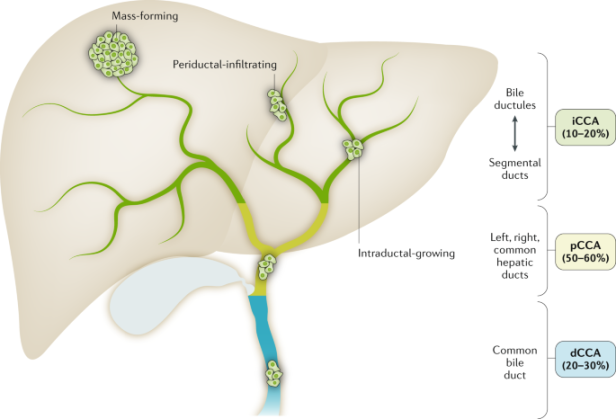
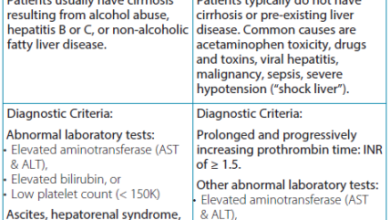
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that originates in the bile ducts. It typically presents with symptoms such as abdominal pain, jaundice, weight loss, and itching. The prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma is poor, as it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited.
Causes
The exact cause of cholangiocarcinoma is not well understood, but certain risk factors have been identified. These include chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, primary sclerosing cholangitis, liver fluke infection, and exposure to certain chemicals or toxins.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, weight loss, fatigue, itching, and dark urine. These symptoms can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma typically involves imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans, as well as blood tests to assess liver function. A biopsy may also be performed to confirm the presence of cancer cells in the bile ducts.
Treatment
Treatment options for cholangiocarcinoma depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. In some cases, a combination of these treatments may be recommended to improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Cholangiocarcinoma is a challenging cancer to diagnose and treat, but with early detection and appropriate management, outcomes can be improved. Understanding the ICD-10 code for this condition is essential for accurate coding and billing in healthcare settings.
FAQs
1. Is cholangiocarcinoma a common type of cancer?
Cholangiocarcinoma is considered a rare type of cancer, accounting for only a small percentage of all cancer diagnoses.
2. What are the risk factors for developing cholangiocarcinoma?
Some risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma include chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, liver fluke infection, and exposure to certain chemicals or toxins.
3. What are the treatment options for cholangiocarcinoma?
Treatment options for cholangiocarcinoma may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy, depending on the stage of the cancer.
4. What are the symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma?
Common symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma include jaund