What is Severe Aortic Stenosis?
Severe aortic stenosis is a condition in which the aortic valve in the heart becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta. This can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness. If left untreated, severe aortic stenosis can result in heart failure and other serious complications.
Code Information for Severe Aortic Stenosis
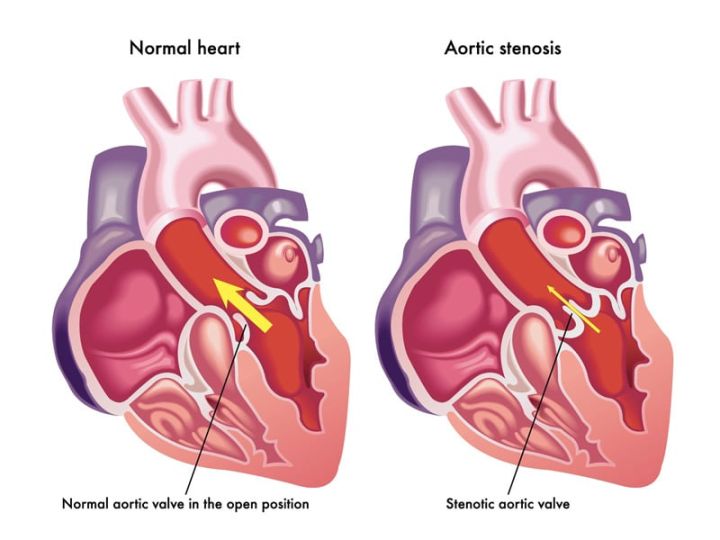
The ICD-10 code for severe aortic stenosis is I35.0. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to this specific condition in medical records and claims for billing purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Severe aortic stenosis falls under DRG 247 – Percutaneous Cardiovascular Procedures with Acute Myocardial Infarction or Angina Pectoris. This DRG is used to group patients with similar diagnoses and treatments for reimbursement purposes.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
For those still using ICD-9 codes, the equivalent code for severe aortic stenosis is 395.0. It is important to remember to update to the ICD-10 code for accurate and compliant coding practices.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for severe aortic stenosis, I35.0, was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems. This change was made to provide more specific and detailed codes for medical conditions.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for severe aortic stenosis include aortic valve stenosis, calcific aortic stenosis, and obstructive aortic valve disease. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the same condition.
Clinical Information
Severe aortic stenosis is most commonly caused by age-related calcification of the aortic valve. Other causes may include congenital heart defects, rheumatic fever, and radiation therapy. Symptoms of severe aortic stenosis typically include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart palpitations.
Causes of Severe Aortic Stenosis
Severe aortic stenosis is often caused by the gradual buildup of calcium deposits on the aortic valve leaflets, leading to narrowing and obstruction of blood flow. Other causes may include congenital heart defects, rheumatic fever, and radiation therapy to the chest area.
Symptoms of Severe Aortic Stenosis
Common symptoms of severe aortic stenosis include chest pain or tightness, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and heart palpitations. These symptoms may worsen over time as the condition progresses.
Diagnosis of Severe Aortic Stenosis
Diagnosis of severe aortic stenosis typically involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests such as echocardiography, and cardiac catheterization. These tests help to assess the severity of the condition and determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment for Severe Aortic Stenosis
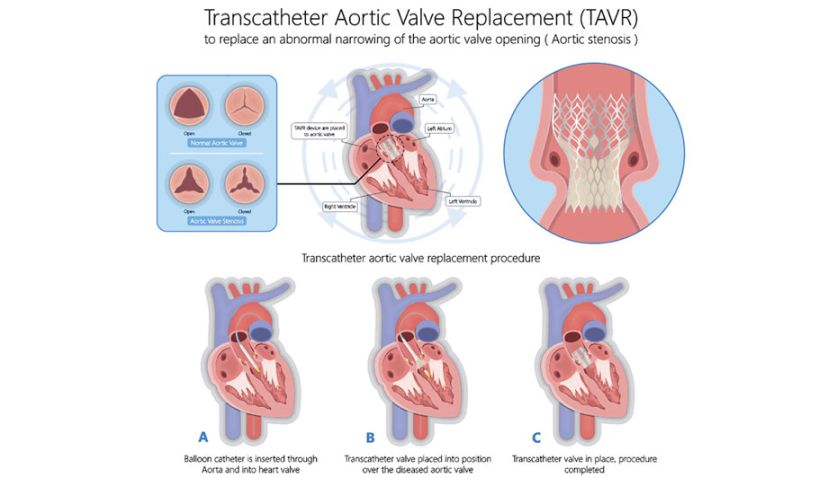
Treatment for severe aortic stenosis may include medications to manage symptoms, minimally invasive procedures such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), or surgical valve replacement. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
Conclusion
Severe aortic stenosis is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to prevent complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for severe aortic stenosis, healthcare providers can effectively manage this condition and improve patient outcomes.
FAQs about Severe Aortic Stenosis
1. Can severe aortic stenosis be cured?
Severe aortic stenosis is a progressive condition that may require ongoing management and treatment, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate care.
2. What are the risk factors for severe aortic stenosis?
Age, genetics, and certain medical conditions such as rheumatic fever or radiation therapy are common risk factors for developing severe aortic stenosis.
3. How is severe aortic stenosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves