Impact Of ICD-10 Coding On Anemia Diagnosis In Chronic Kidney Disease
What is Anemia in CKD?
Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a common complication that occurs when the kidneys are not functioning properly and are unable to produce enough red blood cells. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body, so when there is a deficiency in these cells, it can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Code Information
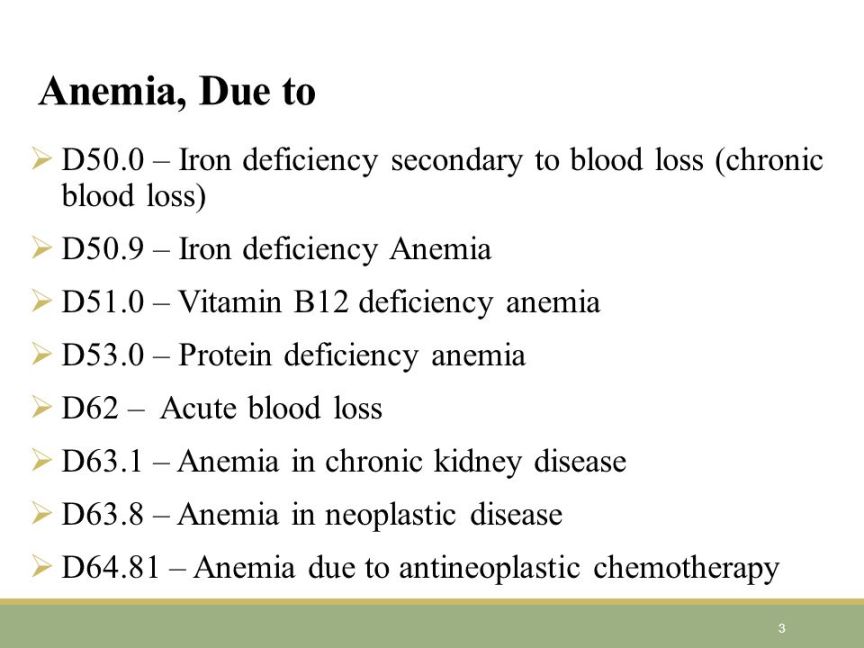
The ICD-10 code for anemia in CKD is D63.1. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
The MS-DRG for anemia in CKD is 682. This DRG is used to classify and group patients with similar diagnoses and treatments related to anemia in chronic kidney disease.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The equivalent ICD-9 code for anemia in CKD is 285.21. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease using the older ICD-9 coding system.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for anemia in CKD was introduced in October 2015 as part of the update to the ICD-10 coding system. This new code allowed for more specific classification and coding of anemia in chronic kidney disease.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for anemia in CKD include renal anemia, kidney disease-related anemia, and anemia of chronic renal failure. These terms are often used interchangeably to refer to anemia that occurs in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Clinical Information
Anemia in CKD is typically caused by a combination of factors, including decreased production of erythropoietin (a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production) and shortened red blood cell survival due to uremic toxins in the blood. Patients with CKD often experience anemia as their kidney function declines.
Causes
The primary cause of anemia in CKD is the decreased production of erythropoietin by the kidneys. This hormone is essential for stimulating red blood cell production in the bone marrow. As kidney function declines in CKD, the production of erythropoietin also decreases, leading to a deficiency of red blood cells in the body.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of anemia in CKD include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, pale skin, and cold hands and feet. These symptoms are due to the decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, resulting in reduced oxygen delivery to tissues and organs throughout the body.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of anemia in CKD is typically made through blood tests that measure the levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and erythropoietin in the blood. Additionally, other tests such as a complete blood count (CBC) and renal function tests may be performed to assess kidney function and evaluate the severity of the anemia.
Treatment
The treatment of anemia in CKD often involves the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to stimulate red blood cell production. These medications are usually administered by injection and help increase the levels of hemoglobin in the blood. In some cases, iron supplementation may also be necessary to support red blood cell production.
Conclusion
Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease is a common complication that can have significant impacts on a patient’s quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for anemia in CKD, healthcare providers can better manage this condition and improve outcomes for patients with chronic kidney disease.
FAQs
1. How common is anemia in CKD?
Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease, affecting a significant number of patients with CKD.
2. How is anemia in CKD diagnosed?
Anemia in CKD is diagnosed through blood tests that measure levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and erythropoietin in the blood.
3. What are the treatment options for anemia in CKD?
Treatment options for anemia in CKD include the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (