Peyronie’s Disease: Understanding The Diagnosis Codes In ICD-10
What is Peyronie’s Disease?
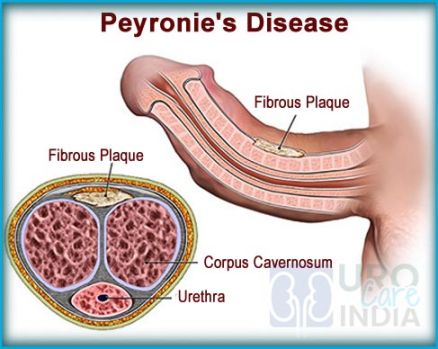
Peyronie’s disease is a condition characterized by the presence of fibrous scar tissue in the penis, which can cause curvature or deformity during an erection. This condition can result in pain, discomfort, and difficulty with sexual intercourse.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for Peyronie’s disease is N48.6. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to this condition in medical records and billing processes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
There are no specific MS-DRGs assigned to Peyronie’s disease, as it is typically managed on an outpatient basis. However, the condition may be associated with other MS-DRGs depending on the treatment required.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The ICD-9 code for Peyronie’s disease is 607.95. This code was used prior to the implementation of the ICD-10 coding system and may still be referenced in some older medical records.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for Peyronie’s disease, N48.6, was introduced in the 2017 version of the International Classification of Diseases coding system. This code replaced the previous ICD-9 code, 607.95.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for Peyronie’s disease include penile fibrosis, penile curvature, and fibrous plaques in the penis.
Clinical Information
Peyronie’s disease is thought to be caused by trauma or injury to the penis, which can lead to the formation of scar tissue. This scar tissue can cause the penis to curve or bend during an erection, resulting in pain and difficulty with sexual activity.
Causes
The exact cause of Peyronie’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to be related to trauma or injury to the penis. This can occur during sexual activity, accidents, or other forms of physical trauma.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Peyronie’s disease include penile curvature, pain during erection, difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, and plaque or lumps in the penis. These symptoms can vary in severity and may worsen over time.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Peyronie’s disease is typically based on a physical examination, medical history, and possibly imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. A healthcare provider may also inquire about symptoms and perform additional tests to rule out other conditions.
Treatment
Treatment for Peyronie’s disease may include medications, such as collagenase injections or oral medications, to help reduce scar tissue and improve penile curvature. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct severe deformities or restore normal function.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Peyronie’s disease is a condition characterized by fibrous scar tissue in the penis, which can cause curvature, pain, and difficulty with sexual activity. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing this condition and improving quality of life for affected individuals.
FAQs
1. Can Peyronie’s disease be cured?
2. What are the risk factors for developing Peyronie’s disease?
3. Is Peyronie’s disease hereditary?
4. How common is Peyronie’s disease?
5. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Peyronie’s disease?