Understanding ICD-10 Codes For Aortic Root Enlargement
What is ICD-10 Aortic Root Enlargement?
ICD-10 Aortic Root Enlargement is a medical condition characterized by the dilation or enlargement of the aortic root, which is the section of the aorta that is closest to the heart. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and connective tissue disorders.
Code Information
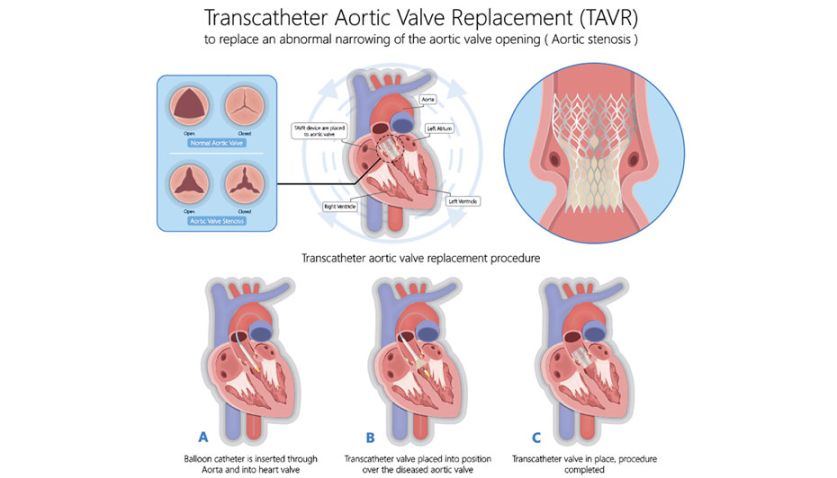
The ICD-10 code for Aortic Root Enlargement is I71.01. This code falls under the category of Diseases of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries (I70-I79) and specifically pertains to Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

The MS-DRG for Aortic Root Enlargement is DRG 112 – Peripheral Vascular Disorders with MCC (Major Complications or Comorbidities) or DRG 113 – Peripheral Vascular Disorders without MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
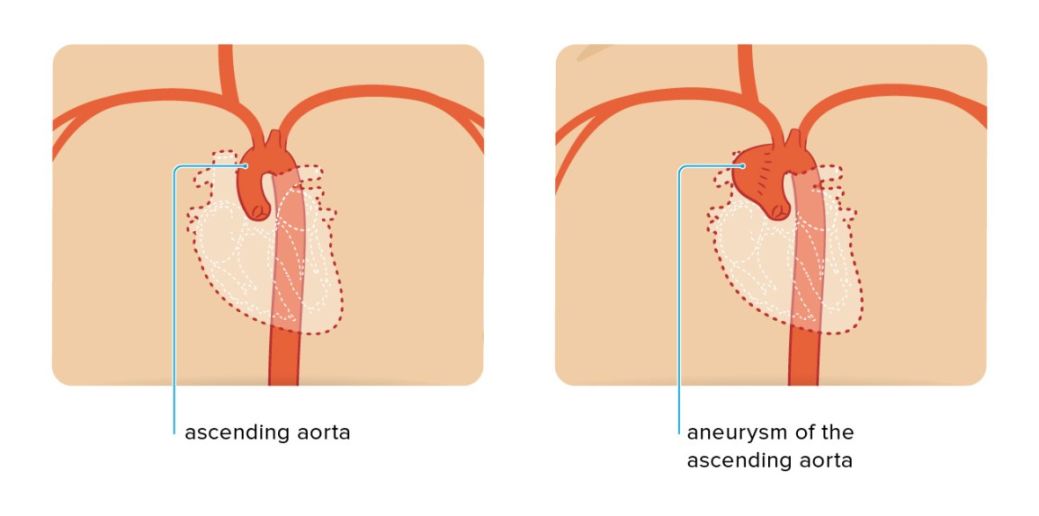
The equivalent ICD-9 code for Aortic Root Enlargement is 441.1 – Aortic aneurysm of thoracic aorta.
Code History
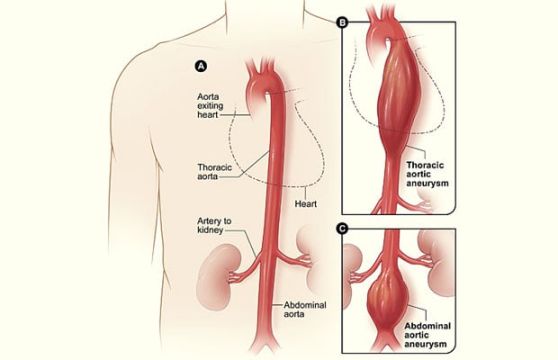
The ICD-10 code for Aortic Root Enlargement was introduced in October 2015 as part of the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases.
Approximate Synonyms
Aneurysm of aorta
Aortic dilation
Aortic root dilatation
Clinical Information
Aortic Root Enlargement can lead to serious complications, such as aortic dissection, aortic regurgitation, and even aortic rupture. It is important for individuals with this condition to receive regular monitoring and treatment to prevent these complications.
Causes
The causes of Aortic Root Enlargement can vary, but some common factors include high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, genetic predisposition, connective tissue disorders (such as Marfan syndrome), and a history of heart valve disease.
Symptoms
Some individuals with Aortic Root Enlargement may not experience any symptoms, while others may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue. In severe cases, symptoms of aortic dissection or rupture may occur, including sudden severe chest or back pain, loss of consciousness, and shock.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Aortic Root Enlargement typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests (such as echocardiography, CT scan, or MRI), and possibly genetic testing. It is important for individuals with risk factors for this condition to undergo regular screening to detect any changes in the size of the aortic root.
Treatment
The treatment of Aortic Root Enlargement depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some individuals may be able to manage their condition with lifestyle changes (such as blood pressure control and regular exercise), while others may require medication or surgical intervention, such as aortic root replacement or repair.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ICD-10 Aortic Root Enlargement is a serious medical condition that can lead to potentially life-threatening complications. It is important for individuals with this condition to receive regular monitoring and treatment to prevent adverse outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Aortic Root Enlargement, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively.
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for developing Aortic Root Enlargement?
2. Can Aortic Root Enlargement be prevented?
3. How is Aortic Root Enlargement different from Aortic Aneurysm?
4. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Aortic Root Enlargement?
5. What should I do if I experience symptoms of Aortic Root Enlargement?