Understanding Acute Monocytic Leukemia ICD-10 Codes And Treatment Options
What is Acute Monocytic Leukemia ICD 10?
Acute monocytic leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It is characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells, called monocytes, which are a type of immune cell. These abnormal cells can crowd out healthy blood cells, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and an increased risk of infections.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for acute monocytic leukemia is C93.1. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses and procedures in healthcare settings. It is important for accurately documenting and tracking cases of this type of leukemia for research and treatment purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Acute monocytic leukemia is classified under MS-DRG 793 – Full Term Neonate with Major Problems. This DRG category includes cases of serious illnesses or conditions in newborns that require intensive care and treatment.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for acute monocytic leukemia is 205.1. This code was used prior to the implementation of the ICD-10 coding system and is still sometimes referenced in medical records and billing.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for acute monocytic leukemia was introduced in the 10th edition of the International Classification of Diseases, which was published by the World Health Organization in 1992. It replaced the previous ICD-9 code for this condition.
Approximate Synonyms
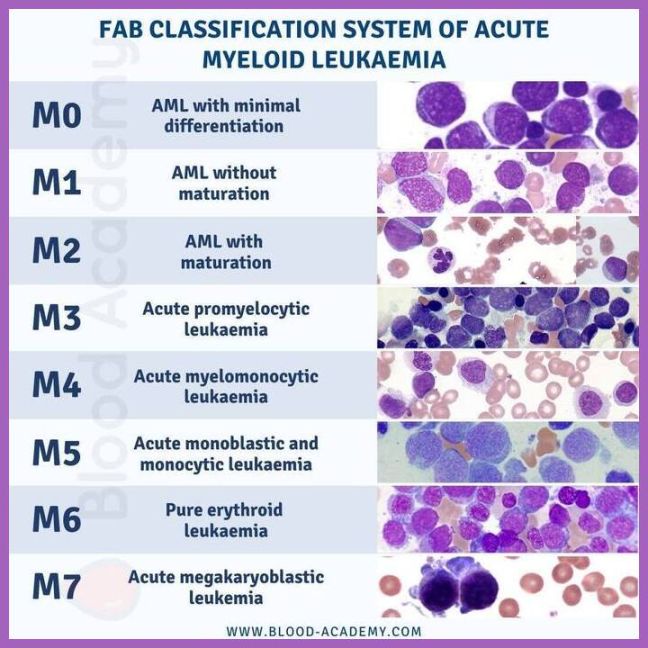
Other terms that may be used to describe acute monocytic leukemia include AML-M5, acute myelomonocytic leukemia, and acute myeloid leukemia with monocytic differentiation. These terms are used interchangeably in medical literature and coding.
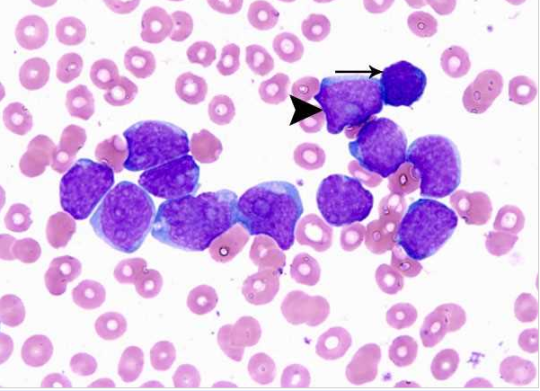
Clinical Information
Acute monocytic leukemia is a rare and aggressive form of leukemia that requires prompt and aggressive treatment. It is typically diagnosed through blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and imaging studies. Treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplants.
Causes
The exact cause of acute monocytic leukemia is unknown, but it is believed to result from genetic mutations that cause abnormal growth and proliferation of white blood cells. Risk factors for developing this type of leukemia may include exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, or genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
Symptoms of acute monocytic leukemia may include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, easy bruising or bleeding, fever, and frequent infections. Patients may also experience bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, and weight loss. It is important to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or worsen.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing acute monocytic leukemia typically involves a thorough physical examination, blood tests to evaluate white blood cell counts and genetic markers, bone marrow biopsies, and imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs. A definitive diagnosis can be made by analyzing the presence of abnormal monocytes in the blood and bone marrow.
Treatment
Treatment for acute monocytic leukemia may involve a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplants. The goal of treatment is to eliminate the abnormal white blood cells and restore healthy blood cell production. Patients may also receive supportive care to manage symptoms and side effects of treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, acute monocytic leukemia is a rare and aggressive form of leukemia that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. The ICD-10 code for this condition is C93.1, and it falls under MS-DRG 793. Patients with this type of leukemia may experience a range of symptoms, and treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplants.
FAQs
1. Is acute monocytic leukemia curable?
While there is no definitive cure for acute monocytic leukemia, treatment options can help manage the disease and improve quality of life.
2. What are the risk factors for developing acute monocytic leukemia?
Risk factors may include exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, or genetic predisposition.
3. How is acute monocytic leukemia diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and imaging studies.
4. What are the common symptoms of acute monocytic leukemia?
Sym