Cracking The Code: ICD-10 For Calcified Coronary Artery Disease
What is Calcified Coronary Artery Disease ICD 10?
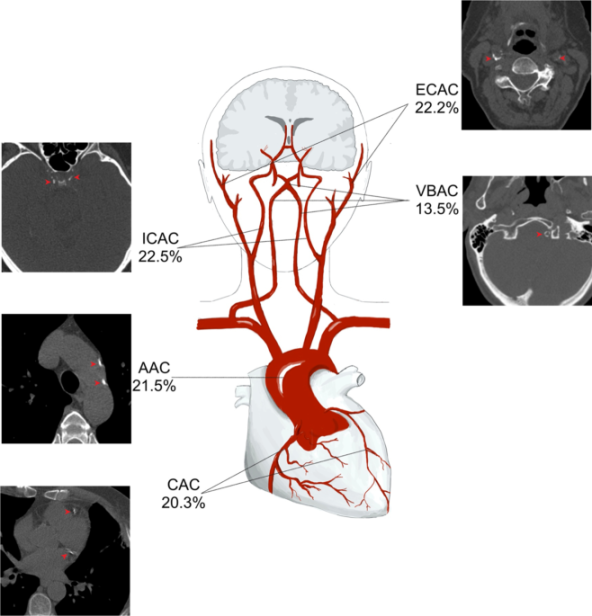
Calcified Coronary Artery Disease ICD 10 is a medical condition where there is a buildup of calcium in the walls of the coronary arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This calcification can lead to narrowing or blockages in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow to the heart and increase the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular problems.
Code Information
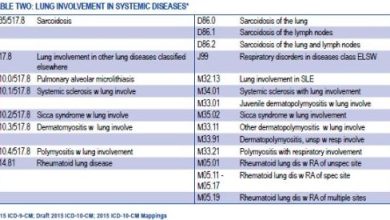
The ICD-10 code for calcified coronary artery disease is I25.8. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to coronary artery disease with other specified forms and is an important tool for healthcare providers to accurately document and track this condition.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
When it comes to the Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Group (MS-DRG) system, calcified coronary artery disease falls under DRG 282 – Acute Myocardial Infarction, Discharged Alive with MCC. This DRG is used to classify patients with acute heart attacks and other related conditions, including calcified coronary artery disease, for the purpose of reimbursement and resource allocation.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

In the older ICD-9 coding system, calcified coronary artery disease is classified under code 414.8 – Other specified forms of chronic ischemic heart disease. This code is used to document and track coronary artery disease in patients and is essential for accurate coding and billing purposes.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for calcified coronary artery disease, I25.8, was introduced in 2015 as part of the tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases. This updated coding system provided more specific and detailed codes for various medical conditions, including calcified coronary artery disease, to improve accuracy and efficiency in healthcare documentation.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for calcified coronary artery disease include coronary artery calcification, coronary artery sclerosis, and coronary artery stenosis. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the same condition of calcium buildup in the coronary arteries that can lead to heart complications.
Clinical Information
Calcified coronary artery disease is a progressive condition that develops over time as calcium deposits accumulate in the walls of the coronary arteries. These deposits can harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle and increasing the risk of heart attacks, angina, and other cardiovascular problems.
Causes
The exact cause of calcified coronary artery disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a result of a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Risk factors for developing this condition include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms
Symptoms of calcified coronary artery disease can vary depending on the severity of the blockages in the arteries. Common symptoms include chest pain or discomfort (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness, and dizziness. In some cases, the first sign of this condition may be a heart attack.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing calcified coronary artery disease typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, imaging tests (such as coronary angiography or CT scans), and blood tests to assess cholesterol and other risk factors. These diagnostic tests help healthcare providers determine the extent of calcification in the coronary arteries and develop a treatment plan.
Treatment
Treatment for calcified coronary artery disease aims to manage symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall heart health. This may include lifestyle changes (such as diet and exercise), medications (such as statins and blood pressure-lowering drugs), procedures (such as angioplasty or bypass surgery), and cardiac rehabilitation to help patients recover and prevent future heart problems.
Conclusion
Calcified coronary artery disease is a serious condition that can significantly impact heart health and overall well-being. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing this condition and reducing the risk of heart complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for calcified coronary artery disease, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart health and improve their quality of life.
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for developing calcified coronary artery disease?
2. What are the common symptoms of calcified coronary artery disease?
3. How is