Navigating ICD-10 Coding For Asthmatic Bronchitis
What is ICD 10 code for bronchitis asthmatic?
ICD-10 code for bronchitis asthmatic is J45.901. This code is used to classify and code bronchitis asthmatic in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10).
Code Information
ICD-10 code J45.901 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
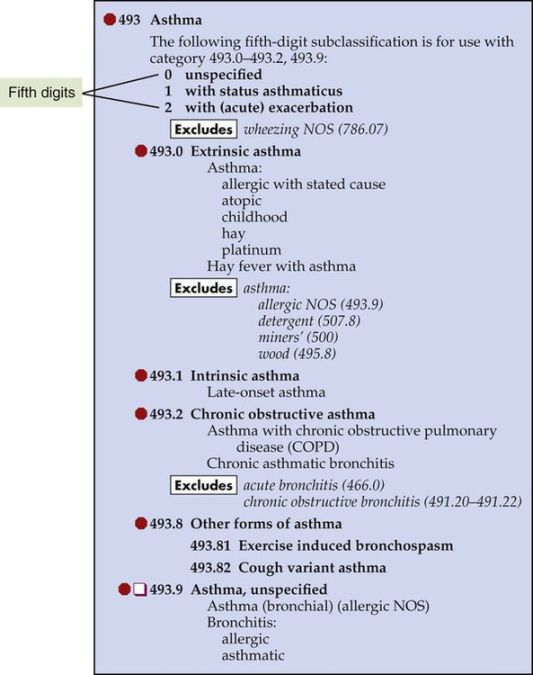
The Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Group (MS-DRG) is a system of classification used by Medicare to determine payment for inpatient hospital services. The MS-DRG for bronchitis asthmatic is MS-DRG 201.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for bronchitis asthmatic is 493.9.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for bronchitis asthmatic was first introduced on October 1, 2015, as part of the U.S. health system’s transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for bronchitis asthmatic include asthmatic bronchitis, reactive airway disease, and bronchial asthma.
Clinical Information

Bronchitis asthmatic is a condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It is commonly associated with asthma and can cause symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The exact cause of bronchitis asthmatic is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Triggers for bronchitis asthmatic can include allergens, air pollution, respiratory infections, and smoking.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of bronchitis asthmatic include wheezing, coughing (often with mucus), chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can vary in severity and may worsen with physical activity or exposure to triggers.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing bronchitis asthmatic typically involves a physical exam, medical history review, and lung function tests such as spirometry. Additional tests may be conducted to rule out other respiratory conditions and to assess the severity of the disease.
Treatment
Treatment for bronchitis asthmatic often includes medications such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and inhaled medications to help control inflammation and open the airways. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and quitting smoking, can also help manage symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bronchitis asthmatic is a common respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes and is commonly associated with asthma. Proper diagnosis and management of bronchitis asthmatic can help control symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
FAQs
1. Is bronchitis asthmatic a serious condition?
While bronchitis asthmatic can be a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, it is not typically considered life-threatening with proper treatment.
2. Can bronchitis asthmatic be prevented?
While the exact cause of bronchitis asthmatic is not fully understood, avoiding triggers such as allergens and smoking can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
3. What is the difference between bronchitis asthmatic and regular bronchitis?
Bronchitis asthmatic is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes and is often associated with asthma, while regular bronchitis is typically caused by a viral or bacterial infection.
4. How is bronchitis asthmatic treated?
Treatment for bronchitis asthmatic often includes medications such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and inhaled medications to help control inflammation and open the airways.
5. Can bronchitis asthmatic be cured?
While there is no cure for bronchitis asthmatic,