Understanding ICD-10 Codes For Mitral Regurgitation: Diagnosis And Treatment
What is ICD-10 Mitral Regurg?
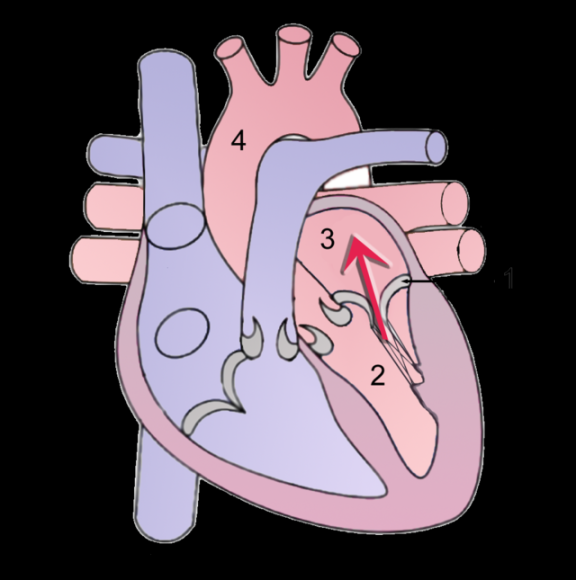
ICD-10 Mitral regurgitation is a medical condition characterized by the backward flow of blood through the mitral valve of the heart. This condition occurs when the valve does not close properly, allowing blood to leak back into the left atrium. Mitral regurgitation can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, including heart failure and arrhythmias.
Code Information

The ICD-10 code for mitral regurgitation is I34.1. This code is used to classify and track cases of mitral regurgitation in medical records and billing systems. It is important for accurate coding and billing purposes to ensure proper reimbursement and treatment.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Patients with mitral regurgitation may be assigned to MS-DRG 216 – Cardiac valve and other major cardiothoracic procedures with cardiac catheterization. This DRG is used to categorize patients who undergo procedures related to heart valves, including those with mitral regurgitation.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The equivalent ICD-9 code for mitral regurgitation is 424.0. This code was used prior to the implementation of ICD-10 and is still sometimes referenced for historical purposes or in certain situations where ICD-10 codes are not available.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for mitral regurgitation was first introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 code sets. It replaced the previous ICD-9 code 424.0 and provided more detailed and specific classification for mitral regurgitation cases.
Approximate Synonyms
MR – Mitral regurgitation
Mitral insufficiency
Regurgitation, mitral valve
Clinical Information
Mitral regurgitation is often caused by structural abnormalities in the mitral valve, such as prolapse or degeneration. Other causes may include infections, rheumatic heart disease, or congenital defects. Symptoms of mitral regurgitation can vary depending on the severity of the condition and may include fatigue, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
Causes
Mitral regurgitation can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Structural abnormalities in the mitral valve
Infections, such as endocarditis
Rheumatic heart disease
Cardiomyopathy
Symptoms
Common symptoms of mitral regurgitation may include:
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Persistent cough
Palpitations
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of mitral regurgitation may involve a physical exam, imaging tests such as echocardiography, and other diagnostic procedures. Treatment options for mitral regurgitation may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery to repair or replace the mitral valve.
Treatment
Treatment for mitral regurgitation may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual patient’s needs. Options may include:
Medication to manage symptoms and reduce complications
Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise modifications
Surgical repair or replacement of the mitral valve
Conclusion
Mitral regurgitation is a serious medical condition that can lead to complications if left untreated. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing symptoms and improving outcomes for patients with this condition. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for mitral regurgitation, healthcare providers can provide effective care for affected individuals.
FAQs:
1. Can mitral regurgitation be cured?
2. What are the long-term effects of untreated mitral regurgitation?
3. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage mitral regurgitation?
4. How is mitral regurgitation diagnosed?
5. What surgical options are available for treating mitral regurgitation?