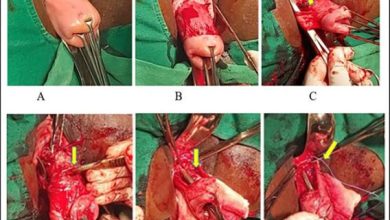
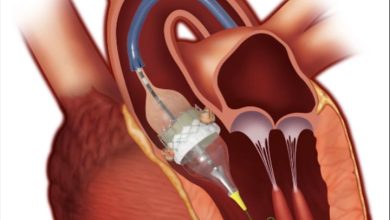
A Closer Look At ICD-10 Code For Aortic Valve Stenosis: I35.0
What is Aortic Valve Stenosis?
Aortic valve stenosis is a condition in which the aortic valve in the heart becomes narrowed, preventing the valve from opening fully and obstructing the flow of blood from the heart to the rest of the body. This can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for aortic valve stenosis is I35.0.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

The MS-DRG for aortic valve stenosis is 226.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The ICD-9 code for aortic valve stenosis is 424.1.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for aortic valve stenosis was introduced in 2015 as part of the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to refer to aortic valve stenosis include aortic stenosis and aortic valve disease.
Clinical Information
Aortic valve stenosis is most commonly caused by the build-up of calcium deposits on the valve, which can lead to the valve becoming stiff and narrowed. Other causes include congenital heart defects and rheumatic fever.
Causes
The main cause of aortic valve stenosis is the build-up of calcium deposits on the valve. This can happen as a person ages, or it can be caused by other factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or smoking.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of aortic valve stenosis include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and fainting. Some people may also experience heart palpitations or a heart murmur.
Diagnosis
Aortic valve stenosis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as echocardiography, cardiac MRI, or cardiac catheterization.
Treatment
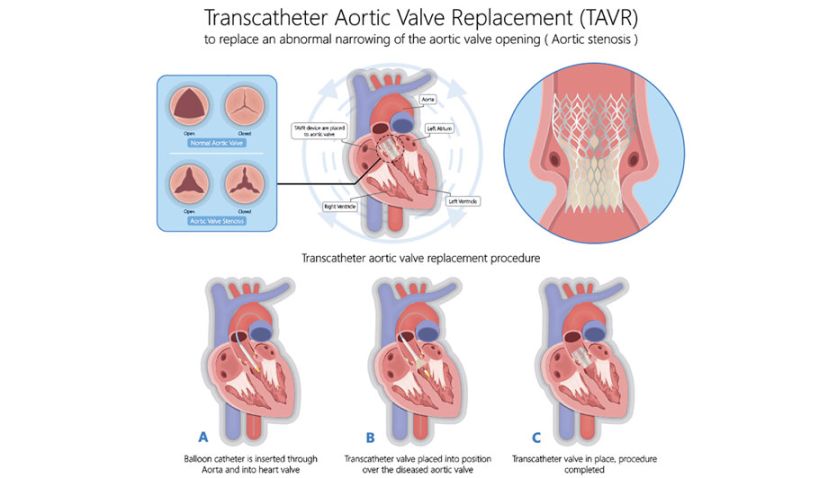
Treatment for aortic valve stenosis may include medications to manage symptoms, surgical repair or replacement of the valve, or a minimally invasive procedure known as TAVR (transcatheter aortic valve replacement).
Conclusion
Aortic valve stenosis is a serious condition that can lead to complications if left untreated. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of aortic valve stenosis and to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and management of the condition.
FAQs
1. Can aortic valve stenosis be prevented?
2. How is aortic valve stenosis diagnosed?
3. What are the treatment options for aortic valve stenosis?
4. Is aortic valve stenosis a common condition?
5. What is the prognosis for someone with aortic valve stenosis?