Cracking The Code: Understanding ICD-10 For Hidradenitis
What is Hidradenitis?
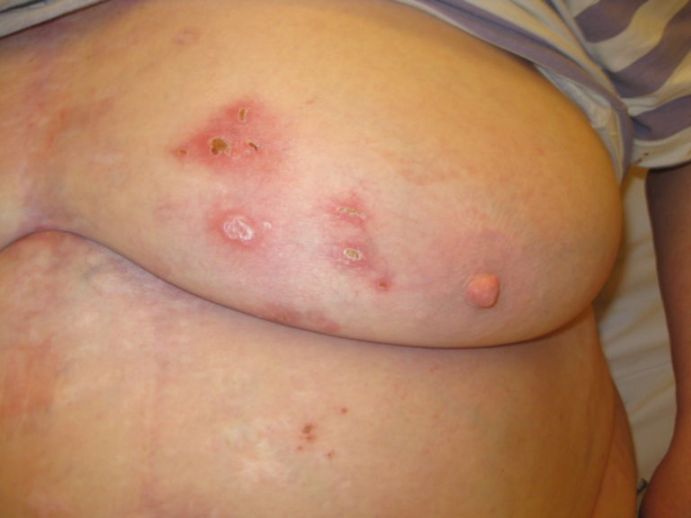
Hidradenitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles and sweat glands. It typically affects areas of the body where there is friction, such as the armpits, groin, and buttocks. The condition can cause painful nodules, abscesses, and scarring.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for hidradenitis is L73.2. This code is used to classify the condition in medical records and for billing purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

Hidradenitis falls under MS-DRG 606 – Minor Skin Disorders with MCC (Major Complications or Comorbidities) or CC (Complications or Comorbidities). This DRG is used to categorize patients with skin disorders for reimbursement purposes.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The ICD-9 code for hidradenitis is 705.83. This code was used prior to the implementation of the ICD-10 coding system and is still sometimes referenced in medical records.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for hidradenitis was introduced in 2015 as part of the updated coding system. This change was made to improve the accuracy and specificity of medical coding.
Approximate Synonyms
Other names for hidradenitis include acne inversa and Verneuil’s disease. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the same condition.
Clinical Information

Hidradenitis is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. The condition is more common in women and tends to develop during adolescence or early adulthood.
Causes
The exact cause of hidradenitis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to inflammation of the hair follicles and sweat glands. Factors such as obesity, smoking, and a family history of the condition may increase the risk of developing hidradenitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hidradenitis can vary in severity and may include painful nodules, abscesses, and scarring. The condition can also cause itching, burning, and discomfort in affected areas of the body.
Diagnosis
Hidradenitis is typically diagnosed based on a physical examination and medical history. In some cases, a biopsy or imaging tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment
Treatment for hidradenitis usually involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and surgical procedures. Medications such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs may help to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. Lifestyle changes such as weight loss and smoking cessation can also improve symptoms. In severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to drain abscesses and remove scar tissue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hidradenitis is a chronic skin condition that can cause pain and discomfort. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to managing symptoms and preventing complications. By understanding the ICD-10 code for hidradenitis and its clinical implications, healthcare providers can effectively document and treat patients with this condition.
FAQs
Can hidradenitis be cured? Hidradenitis is a chronic condition that cannot be cured, but symptoms can be managed with proper treatment.
Is hidradenitis contagious? Hidradenitis is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
Can hidradenitis cause complications? In severe cases, hidradenitis can lead to complications such as scarring, abscesses, and secondary infections.
Is hidradenitis hereditary? While hidradenitis is not directly inherited, there may be a genetic predisposition to developing the condition.
Can hidradenitis be prevented? Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and practicing good hygiene can help reduce the risk of developing hidradenitis.