Understanding ICD-10 Coding For Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
What is ICD-10 for TAVR?
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. It is a medical classification list created by the World Health Organization (WHO) that contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
Code Information
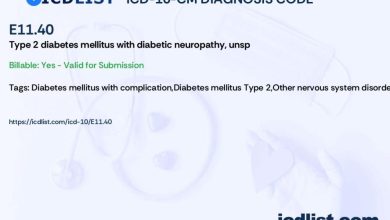
The ICD-10 code for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is Z95.2. This code is used to specify a diagnosis of presence of prosthetic heart valve. It is important for healthcare providers to use this specific code when billing for TAVR procedures.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
The MS-DRG for TAVR is 266 – Endovascular Cardiac Valve Replacement with MCC or 267 – Endovascular Cardiac Valve Replacement without MCC. These DRGs are used by Medicare to classify TAVR procedures for payment purposes.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
To convert the ICD-10 code Z95.2 for TAVR to ICD-9, the corresponding code is V43.3. Healthcare providers may need to use this code when transitioning between different code sets.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for TAVR was introduced in 2016 as part of the regular update cycle of the ICD code set. It replaced the previous ICD-9 code for TAVR, V43.3.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for TAVR include transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) and percutaneous aortic valve replacement. These terms are often used interchangeably with TAVR.
Clinical Information
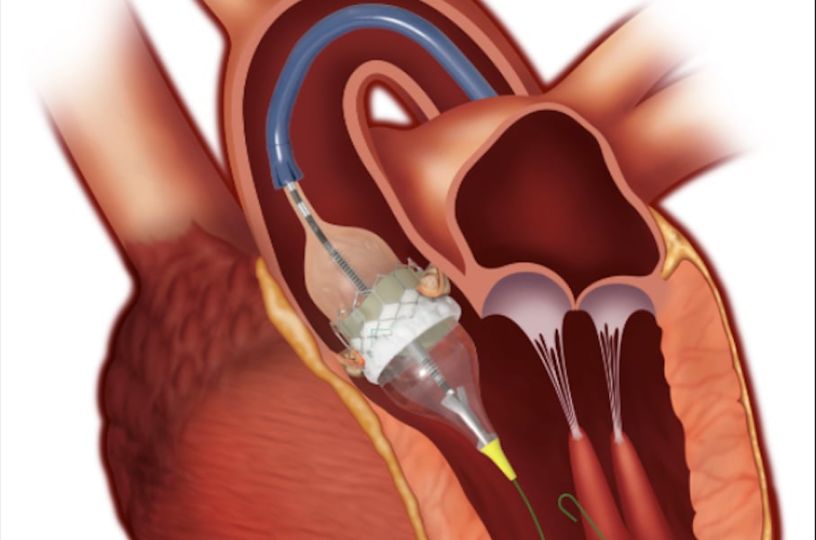
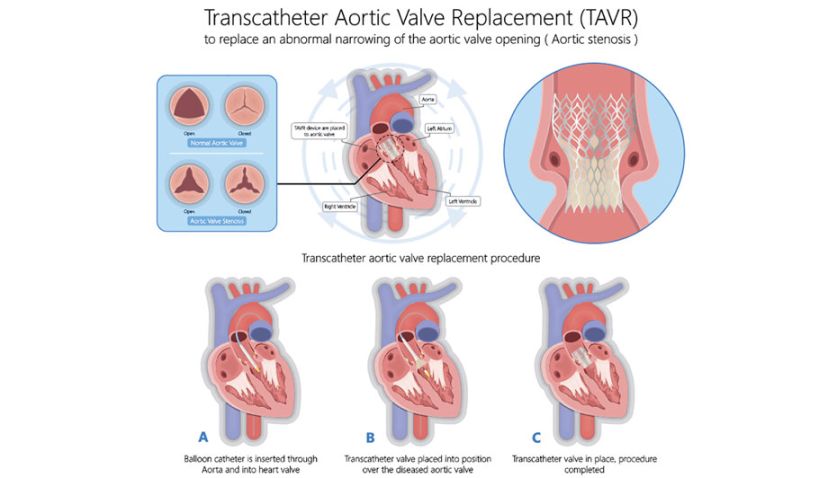
TAVR is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat aortic valve stenosis, a condition where the valve in the heart’s main artery becomes narrowed or stiffened. During TAVR, a new valve is implanted inside the diseased valve using a catheter, avoiding the need for open-heart surgery.
Causes
Aortic valve stenosis can be caused by age-related degeneration, congenital heart defects, or other medical conditions such as rheumatic fever. TAVR is typically recommended for patients who are considered high-risk for traditional open-heart surgery.
Symptoms
Symptoms of aortic valve stenosis may include chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, and fainting. These symptoms can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and may worsen over time if left untreated.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of aortic valve stenosis is typically done through echocardiography, a non-invasive imaging test that allows healthcare providers to visualize the heart valves and assess their function. Additional tests such as cardiac catheterization may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment options for aortic valve stenosis include medication to manage symptoms and surgical interventions such as TAVR or open-heart surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the patient’s overall health and the severity of their condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the ICD-10 code for TAVR is essential for healthcare providers to accurately document and bill for this minimally invasive procedure. TAVR has revolutionized the treatment of aortic valve stenosis, offering a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional open-heart surgery.
FAQs
What is the ICD-10 code for TAVR?
How is TAVR different from open-heart surgery?
What are the benefits of using the specific ICD-10 code for TAVR?
What are the potential complications of TAVR?
How can patients prepare for a TAVR procedure?