Understanding The Importance Of ICD-10 Coding For Hepatitis C Screening
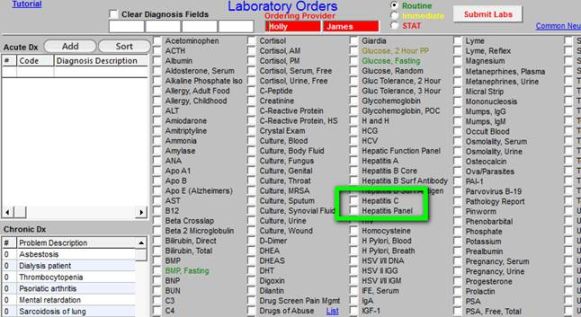
What is ICD 10 Hepatitis C Screening?
ICD-10 Hepatitis C Screening is a diagnostic code used in medical billing and coding to identify patients who are being screened for Hepatitis C. Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation, sometimes leading to serious liver damage. Screening for Hepatitis C is important because early detection can lead to earlier treatment and better outcomes for patients.
Code Information
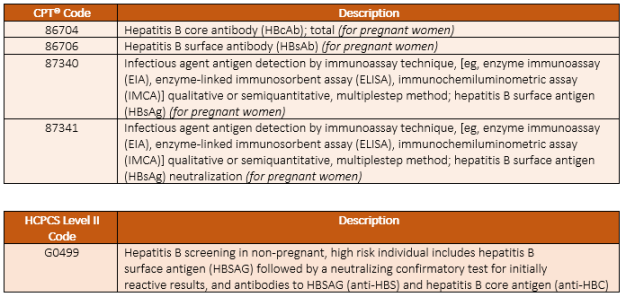
The ICD-10 code for Hepatitis C Screening is Z11.3. This code is used to indicate that a patient is being screened for Hepatitis C, but does not have a confirmed diagnosis of the infection.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
There are no specific MS-DRG codes related to Hepatitis C Screening, as screening tests are typically performed on an outpatient basis.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The equivalent ICD-9 code for Hepatitis C Screening is V73.89. This code is used to indicate a special screening examination for other specified viral diseases.
Code History
The ICD-10 code Z11.3 for Hepatitis C Screening was introduced in 2015 as part of the update to the ICD-10 coding system.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to describe Hepatitis C Screening include Hep C Screening, HCV Screening, and Hepatitis C Antibody Test.
Clinical Information
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus that primarily affects the liver. It is spread through contact with infected blood, most commonly through sharing needles or other drug injection equipment. Hepatitis C can also be transmitted through sexual contact and from mother to baby during childbirth.
Causes
The main cause of Hepatitis C is infection with the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). The virus is most commonly spread through contact with infected blood.
Symptoms
Many people with Hepatitis C do not experience any symptoms, especially in the early stages of infection. However, some people may experience fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Hepatitis C is typically done through blood tests that detect the presence of HCV antibodies or the virus itself. Screening for Hepatitis C is recommended for individuals at increased risk of infection, such as those who have injected drugs, received blood transfusions before 1992, or have HIV.
Treatment
Treatment for Hepatitis C may include antiviral medications that can help clear the virus from the body. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary for patients with advanced liver damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ICD-10 Hepatitis C Screening is an important diagnostic code used to identify patients who are being screened for Hepatitis C. Early detection and treatment of Hepatitis C can help prevent serious liver damage and improve patient outcomes.
FAQs
1. Is Hepatitis C Screening covered by insurance?
Most insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid, cover Hepatitis C Screening for individuals at increased risk of infection.
2. How often should I get screened for Hepatitis C?
Individuals at increased risk of Hepatitis C infection should be screened at least once, with frequency determined by their healthcare provider.
3. Can Hepatitis C be cured?
Yes, Hepatitis C can be cured with antiviral medications that can clear the virus from the body.
4. Are there any side effects of Hepatitis C treatment?
Some common side effects of Hepatitis C treatment may include fatigue, nausea, and headache. However, these side effects are usually mild and temporary.
5. What should I do if I test positive for Hepatitis C?
If you test positive for Hepatitis C, it is important to follow up with your healthcare provider for further testing and treatment options. They can help develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.