Understanding Metastatic Adenocarcinoma Of Lung: ICD-10 Codes And Diagnosis
What is Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of Lung ICD 10?
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung is a type of cancer that starts in the cells of the lung and spreads to other parts of the body. It is classified under the ICD-10 code C34.9, which specifically refers to malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of right bronchus or lung.
Code Information
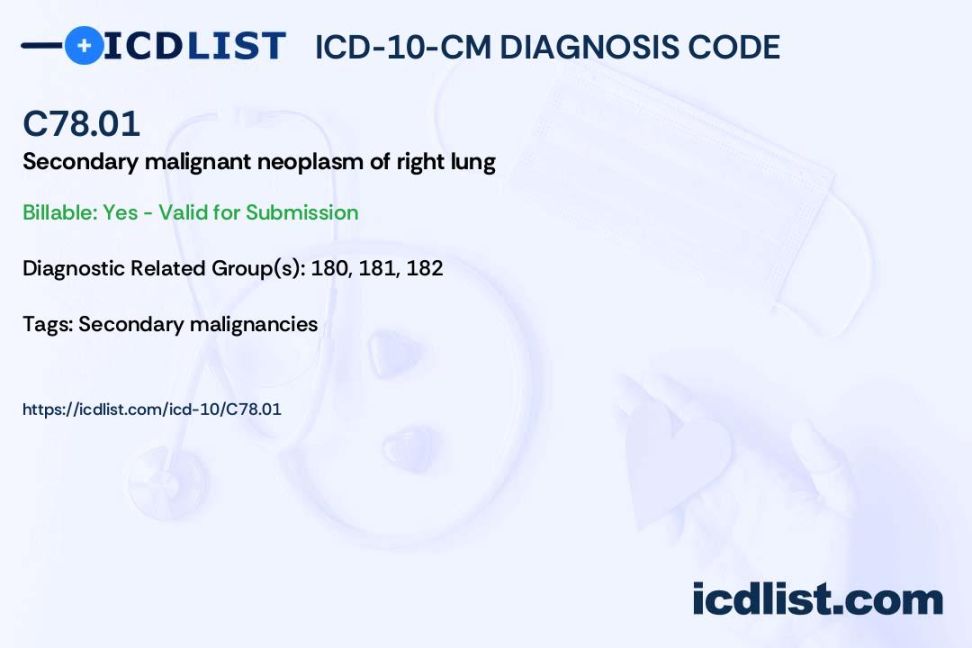
The ICD-10 code for metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung is used by healthcare providers to accurately document and track the diagnosis of this type of cancer. This code helps in ensuring proper treatment and billing for the services provided.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

Metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung falls under the MS-DRG 166 – Other Respiratory System Diagnoses with MCC (Major Complications or Comorbidities). This DRG categorizes patients with respiratory system conditions that have significant complications or comorbidities.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
For those still using the ICD-9 coding system, metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung can be coded as 162.9 – Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung, unspecified. It is important to transition to the ICD-10 system for accurate and detailed coding.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10. This change was made to improve specificity and accuracy in coding for various medical conditions, including cancer.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to describe metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung include secondary lung cancer, metastatic lung tumor, and advanced lung adenocarcinoma. These synonyms are helpful in understanding the nature of the disease.
Clinical Information
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. It often presents with symptoms such as persistent cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and weight loss. Imaging tests like CT scans and biopsies are commonly used to confirm the diagnosis.
Causes
The exact cause of metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung is not fully understood, but it is believed to be linked to factors such as smoking, exposure to asbestos and other carcinogens, and genetic predisposition. Early detection and prevention are key in reducing the risk of developing this type of cancer.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung include coughing up blood, chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing, hoarseness, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms may vary depending on the extent of the cancer spread.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung typically involves a combination of imaging tests (such as CT scans and PET scans), biopsies, and laboratory tests. The diagnosis is confirmed based on the presence of cancer cells in the lung tissue and evidence of metastasis to other organs.
Treatment
Treatment for metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and other individual factors. Palliative care may also be recommended to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung is a serious and complex condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. Early detection, accurate coding, and appropriate interventions are crucial in improving outcomes for patients with this type of cancer.
FAQs
What are the risk factors for metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung?
Common risk factors include smoking, exposure to asbestos, family history of lung cancer, and certain genetic mutations.
How is metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung treated?
Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.