Managing Moderate Persistent Asthma With Acute Exacerbation: Understanding ICD-10 Codes
What is Moderate Persistent Asthma with Acute Exacerbation ICD 10?
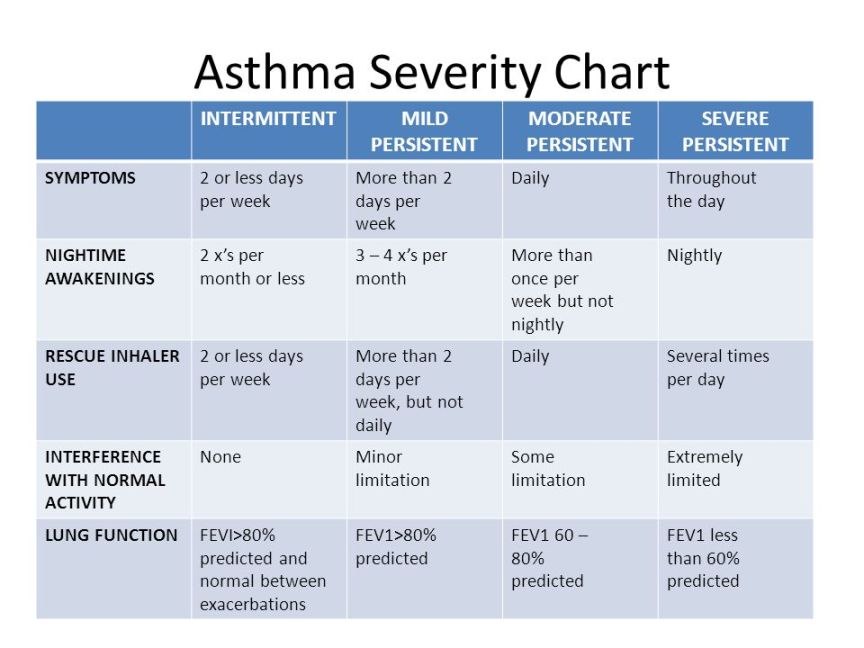
Moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation is a specific medical diagnosis code used in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) coding system. This code is used by healthcare providers to classify and code patients who have asthma that is characterized by symptoms of moderate severity with an acute worsening of symptoms.
Code Information

The ICD-10 code for moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation is J45.41. This code is used to indicate that the patient has asthma that is classified as moderate persistent and is currently experiencing an acute exacerbation of their symptoms.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
When a patient is diagnosed with moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation, they may be assigned to a specific Diagnosis Related Group (DRG) for billing purposes. The DRG that is typically assigned for this condition is DRG 202 – Bronchitis and Asthma with CC/MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
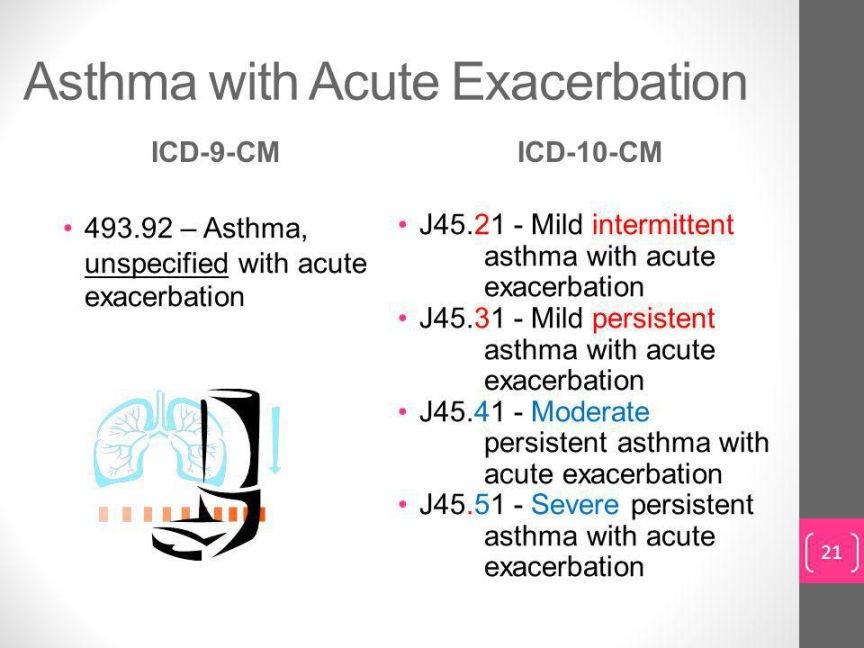
The equivalent ICD-9 code for moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation is 493.22. This code is used to classify the same condition in the previous coding system, ICD-9.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation was first introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from the ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding system. It is used by healthcare providers to accurately document and bill for this specific type of asthma diagnosis.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation include:
Asthma exacerbation
Moderate asthma exacerbation
Asthma attack
Acute exacerbation of asthma
Clinical Information
Moderate persistent asthma is a type of asthma that is characterized by symptoms that occur on a daily basis and may interfere with daily activities. During an acute exacerbation, the symptoms of asthma worsen suddenly and may require immediate medical attention.
Causes
The exact cause of asthma is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Triggers for asthma exacerbations can vary from person to person and may include allergens, respiratory infections, exercise, and stress.
Symptoms
Symptoms of moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation may include:
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Coughing
Wheezing
Difficulty breathing
Diagnosis
Diagnosing moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation typically involves a physical exam, medical history review, and pulmonary function tests. Additional tests, such as allergy testing or imaging studies, may be done to rule out other possible causes of symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment for moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation may include:
Short-acting bronchodilators to relieve symptoms
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Long-term control medications to prevent symptoms
Avoiding triggers and allergens
Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider
Conclusion
In conclusion, moderate persistent asthma with acute exacerbation is a specific type of asthma that is characterized by symptoms of moderate severity with sudden worsening of symptoms. Proper diagnosis and management of this condition are essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life for patients.
FAQs
1. Can asthma be cured?
Asthma is a chronic condition that cannot be cured, but it can be effectively managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes.
2. Are asthma exacerbations preventable?
While asthma exacerbations cannot always be completely prevented, taking medications as prescribed, avoiding triggers, and following an asthma action plan can help reduce the frequency and severity of exacerbations.
3. Is asthma hereditary?
Asthma tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition. However, environmental factors also play a significant role in the development of asthma.