Understanding Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency: ICD-10 Diagnosis And Management
What is Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency ICD 10?
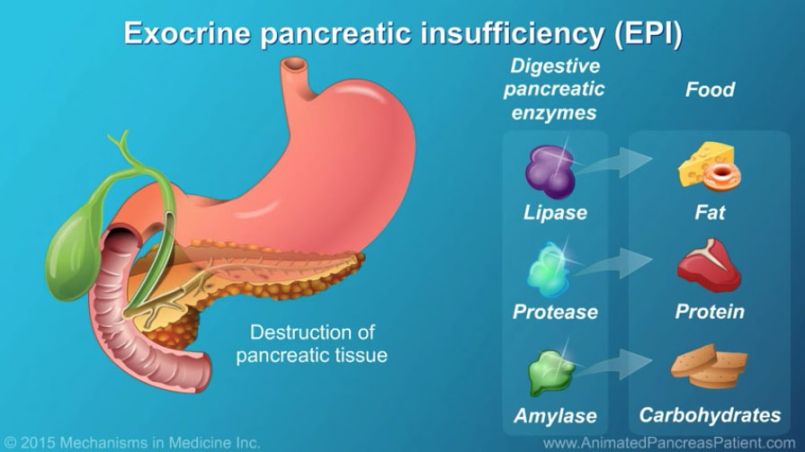
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) is a condition in which the pancreas does not produce enough digestive enzymes to properly break down food in the small intestine. This can lead to malabsorption of nutrients and can cause symptoms such as weight loss, diarrhea, and bloating.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency is K86.1. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to PEI in medical billing and coding.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency falls under MS-DRG 641 – Miscellaneous Disorders of Nutrition, Metabolism, Fluids, and Electrolytes. This DRG is used to classify cases involving disorders related to nutrition and metabolism.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

In the ICD-9 coding system, pancreatic exocrine insufficiency is classified under code 577.1. This code is used to identify conditions related to pancreatic dysfunction.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems. This update allowed for more specific coding of conditions related to pancreatic dysfunction.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to describe pancreatic exocrine insufficiency include exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, pancreatic insufficiency, and pancreatic enzyme deficiency.
Clinical Information
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough digestive enzymes, such as lipase, protease, and amylase, to properly digest food. This can result in malabsorption of nutrients and can lead to symptoms such as steatorrhea (fatty stools), weight loss, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Causes
PEI can be caused by a number of factors, including chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, and autoimmune conditions. In some cases, it may be idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown.
Symptoms
The symptoms of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency can vary, but common symptoms include weight loss, diarrhea, steatorrhea, bloating, abdominal pain, and malnutrition. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of enzyme deficiency.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency typically involves a combination of clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests can measure levels of pancreatic enzymes, while imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs can assess the structure of the pancreas.
Treatment
Treatment for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency aims to replace the deficient digestive enzymes and manage symptoms. This is typically done through pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT), which involves taking oral enzyme supplements with meals to aid in digestion. Dietary modifications may also be recommended to help manage symptoms and improve nutrient absorption.
Conclusion
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency is a condition in which the pancreas does not produce enough digestive enzymes, leading to malabsorption of nutrients and symptoms such as weight loss and diarrhea. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential in managing this condition and improving quality of life for affected individuals.
FAQs
1. What are the common symptoms of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency?
Common symptoms include weight loss, diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain, and malnutrition.
2. What causes pancreatic exocrine insufficiency?
Causes include chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, and autoimmune conditions.
3. How is pancreatic exocrine insufficiency diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
4. What is the treatment for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency?
Treatment typically involves pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy and dietary modifications.
5. What is the ICD-10 code for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency?
The ICD-10 code is K86.1.