Diagnosis And Management Of Severe Aortic Stenosis: ICD-10 Codes And Guidelines
Cracking the Code: Diagnosing Aortic Stenosis
When it comes to the diagnosis and management of severe aortic stenosis, cracking the code is essential. Aortic stenosis is a condition where the aortic valve in the heart narrows, restricting blood flow to the rest of the body. This can lead to serious complications if left untreated, making early diagnosis crucial for effective management.

In order to properly diagnose aortic stenosis, healthcare providers rely on a set of specific ICD-10 codes. These codes are used to classify diseases and medical conditions, allowing for accurate billing and medical recordkeeping. For aortic stenosis, the primary ICD-10 code used is I35.0, which specifies aortic (valve) stenosis. This code helps healthcare providers quickly identify and treat patients with this condition.
In addition to using the correct ICD-10 code, healthcare providers follow specific guidelines for diagnosing aortic stenosis. The first step in diagnosis usually involves a physical examination, where a healthcare provider listens for a heart murmur, a common sign of aortic stenosis. Further diagnostic tests may include an echocardiogram, which provides detailed images of the heart and can confirm the presence of aortic stenosis.

Once a diagnosis is confirmed, it is crucial to begin managing the condition promptly. Guidelines for managing severe aortic stenosis recommend a multifaceted approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors are often prescribed to help manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes play a key role in managing aortic stenosis. Patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking, as these habits can help improve heart health and reduce symptoms of aortic stenosis. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are also important for effective management of the condition.
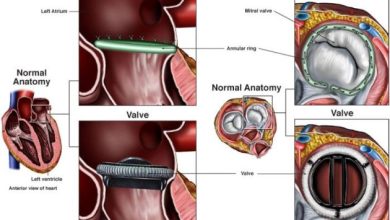
In cases where medication and lifestyle changes are not enough to manage severe aortic stenosis, surgical intervention may be necessary. The most common surgical procedure for aortic stenosis is aortic valve replacement, where the narrowed valve is replaced with a prosthetic valve. This procedure can help improve blood flow and reduce symptoms, ultimately improving quality of life for patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Overall, the diagnosis and management of severe aortic stenosis require a comprehensive approach that involves accurate coding, adherence to guidelines, and collaboration between healthcare providers and patients. By cracking the code and following recommended protocols, healthcare providers can effectively diagnose and manage this serious heart condition, ultimately improving outcomes for patients with aortic stenosis.