Diagnosis And Treatment Of Carotid Artery Stenosis: Understanding ICD-10 Codes
What is Stenosis of Carotid Artery ICD-10?
Stenosis of carotid artery is a condition in which the carotid arteries, which are the major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to a decrease in blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Code Information
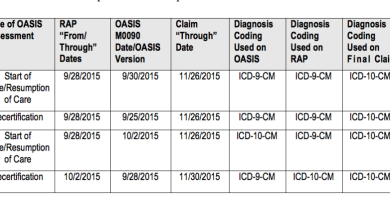
The ICD-10 code for stenosis of carotid artery is I65.2. This code is used to classify this condition in medical records and for billing purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

The MS-DRG for stenosis of carotid artery is MS-DRG 001, which includes procedures for carotid artery stent placement and carotid endarterectomy.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for stenosis of carotid artery is 433.10.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for stenosis of carotid artery was introduced in October 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to describe stenosis of carotid artery include carotid artery disease, carotid artery stenosis, and carotid artery occlusion.
Clinical Information

Stenosis of carotid artery is usually caused by a buildup of plaque in the artery, which can restrict blood flow. This can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, weakness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, and vision problems.
Causes
The main causes of stenosis of carotid artery include atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries, and inflammation of the artery walls. Risk factors for developing this condition include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Symptoms
The symptoms of stenosis of carotid artery can vary depending on the degree of narrowing in the artery. Mild stenosis may not cause any symptoms, while severe stenosis can lead to a stroke or TIA.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of stenosis of carotid artery is typically done through imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. These tests can help determine the extent of blockage in the artery and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment
Treatment for stenosis of carotid artery may include lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. Medications such as statins and blood thinners may also be prescribed to help manage risk factors. In severe cases, procedures such as carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting may be recommended to open up the blocked artery.
Conclusion
Stenosis of carotid artery is a serious condition that can lead to strokes and other complications if left untreated. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of carotid artery stenosis and to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and management of this condition.
FAQs
What are the risk factors for developing stenosis of carotid artery?
How is stenosis of carotid artery diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for stenosis of carotid artery?
Can stenosis of carotid artery be prevented?
What are the long-term effects of untreated stenosis of carotid artery?