Exploring Kappa Light Chain Disease: Understanding The ICD-10 Code
What is Kappa Light Chain Disease ICD 10?
Kappa light chain disease (KLCD) is a rare form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects the production of immunoglobulin light chains. This condition is characterized by the overproduction of kappa light chains, which are part of the antibody molecules that help the body fight infections. In the ICD-10 coding system, KLCD is assigned the code C88.3.
Code Information
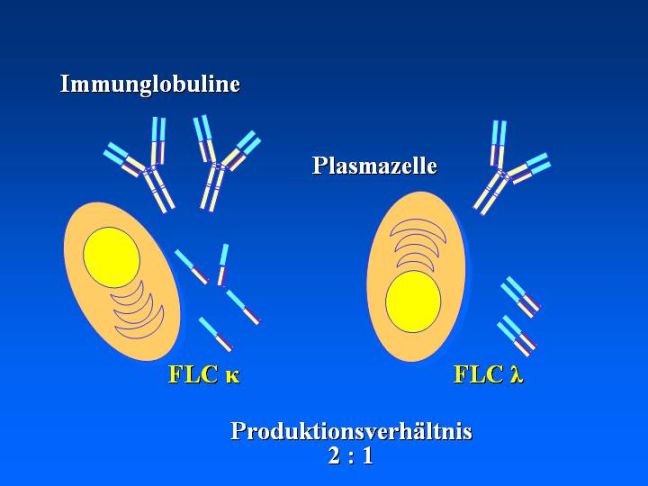
The ICD-10 code for kappa light chain disease is C88.3. This code is used to classify and track cases of KLCD in medical records, billing, and statistical analysis. By using the appropriate ICD-10 code, healthcare providers can accurately document and communicate the diagnosis of KLCD.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
KLCD is typically classified under the Major Hematologic Diagnoses and Disorders MS-DRG 814. This DRG grouping includes a range of hematologic conditions, such as lymphomas, leukemias, and other blood disorders. Patients with KLCD may be admitted to the hospital under this DRG for treatment and management.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
In the ICD-9 coding system, kappa light chain disease is classified under code 273.3. This code is used to track and report cases of KLCD in medical records and billing. Healthcare providers may need to convert between ICD-10 and ICD-9 codes depending on the requirements of the healthcare system or insurance companies.
Code History
The ICD-10 code C88.3 for kappa light chain disease was introduced in the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases. This update expanded and revised the coding system to provide more specific and detailed classifications for various diseases and conditions, including KLCD.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to refer to kappa light chain disease include monoclonal gammopathy, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. These synonyms are used to describe the same condition characterized by the overproduction of kappa light chains in the body.
Clinical Information
Kappa light chain disease is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that primarily affects the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It is characterized by the proliferation of abnormal plasma cells that produce excess kappa light chains, leading to the formation of monoclonal proteins in the blood and urine. Patients with KLCD may experience symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, anemia, and increased risk of infections.
Causes
The exact cause of kappa light chain disease is unknown, but it is believed to be related to genetic mutations and abnormalities in the immune system. Factors that may contribute to the development of KLCD include exposure to environmental toxins, viral infections, and chronic inflammation. Individuals with a family history of lymphomas or other blood cancers may also be at higher risk for developing KLCD.
Symptoms
Patients with kappa light chain disease may experience a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, unintentional weight loss, night sweats, and recurrent infections. Some individuals may also develop anemia, easy bruising, and bleeding problems due to the abnormal production of plasma cells in the bone marrow. As the disease progresses, patients may experience enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, or liver.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing kappa light chain disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may perform blood tests to measure the levels of monoclonal proteins, kidney function, and complete blood count. Imaging studies such as CT scans, MRI, or PET scans may be used to assess the extent of disease involvement in the body. A bone marrow biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis of KLCD.
Treatment
The treatment approach for kappa light chain disease depends on the stage of the disease, overall health of the patient, and individual preferences. Treatment options may include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, stem cell transplantation, and radiation therapy. Patients with KLCD may also benefit from supportive care measures such as blood transfusions, antibiotics, and symptom management. Clinical trials and experimental therapies may be available for patients with refractory or relapsed disease.
Conclusion
Kappa light chain disease is a rare form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma characterized by the overproduction of kappa light chains in the body. The I