Eosinophilic Oesophagitis: Understanding The ICD-10 Code For Diagnosis And Treatment
What is Eosinophilic Oesophagitis ICD 10?
Eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) is a chronic allergic inflammatory disease of the esophagus that is characterized by the presence of a high number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the esophageal tissue. The ICD 10 code for eosinophilic oesophagitis is K20.0.
Code Information
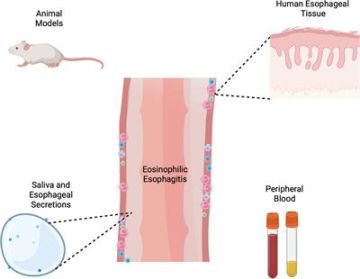
The ICD-10 code for eosinophilic oesophagitis is used by healthcare providers to classify and code diagnoses of this condition in medical records. It helps with tracking and monitoring the prevalence of EoE and assists in treatment planning and research.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Eosinophilic oesophagitis falls under MS-DRG 391 – Esophagitis, Gastroenteritis, and Miscellaneous Digestive Disorders with MCC (Major Complications or Comorbidities) or CC (Complications or Comorbidities). This DRG classification helps determine the payment for inpatient hospital services related to EoE.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

For those still using the ICD-9 coding system, the equivalent code for eosinophilic oesophagitis is 530.13.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for eosinophilic oesophagitis was introduced in the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), which was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1992.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for eosinophilic oesophagitis include allergic esophagitis, EoE, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Clinical Information
Eosinophilic oesophagitis is considered a type of food allergy and is characterized by symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and food impaction. It is more common in individuals with a history of allergies or asthma.
Causes
The exact cause of eosinophilic oesophagitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an allergic response to certain foods or environmental triggers. Genetics and immune system abnormalities may also play a role.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of eosinophilic oesophagitis include dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), chest pain, heartburn, food impaction, and nausea. In children, symptoms may also include feeding difficulties and poor growth.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing eosinophilic oesophagitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, endoscopy with biopsy, and allergy testing. The presence of a high number of eosinophils in the esophageal tissue confirms the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for eosinophilic oesophagitis may involve dietary changes, such as eliminating trigger foods, and medication, such as proton pump inhibitors or corticosteroids. In severe cases, esophageal dilation or allergen immunotherapy may be recommended.
Conclusion
Eosinophilic oesophagitis is a chronic allergic inflammatory disease of the esophagus that can cause significant symptoms and complications. Proper diagnosis and management are essential for improving quality of life and preventing long-term complications.
FAQs:
What are the common symptoms of eosinophilic oesophagitis?
Common symptoms include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and food impaction.
Is eosinophilic oesophagitis related to food allergies?
Yes, EoE is considered a type of food allergy.
How is eosinophilic oesophagitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves endoscopy with biopsy and allergy testing.
What are the treatment options for eosinophilic oesophagitis?
Treatment may involve dietary changes, medication, or procedures like esophageal dilation.
Can eosinophilic oesophagitis be cured?
While there is no cure for EoE, proper management can help control symptoms and improve quality of life.