Understanding Acute On Chronic Systolic CHF In ICD-10 Coding
What is Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF ICD 10?
Acute on Chronic Systolic Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) with ICD-10 code I50.41 is a medical condition that occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This condition can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and abdomen. It is important to accurately code this condition in order to facilitate proper diagnosis and treatment.
Code Information
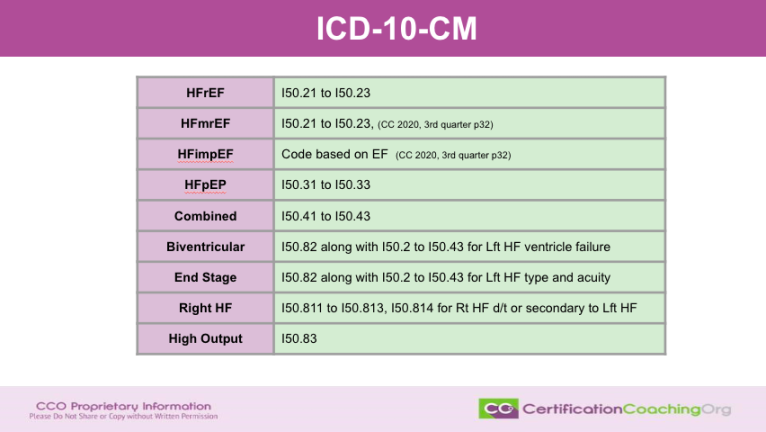
The ICD-10 code for Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF is I50.41. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
In the Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Group (MS-DRG) system, Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF falls under DRG 291 – Heart Failure and Shock with Major Complication or Comorbidity. This grouping helps determine the reimbursement for hospital services related to this condition.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
Prior to the implementation of ICD-10, the equivalent code for Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF was I50.2 in ICD-9. It is important to accurately convert codes when transitioning between code sets to ensure proper billing and reimbursement.
Code History
The ICD-10 code I50.41 for Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF was first introduced in 2015 as part of the updated coding system. This code is used by healthcare providers to accurately document and track cases of this condition.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF include Decompensated Systolic Heart Failure, Acute Decompensated Heart Failure, and Acute Systolic Heart Failure Exacerbation. These terms may be used interchangeably with the official ICD-10 code.
Clinical Information
Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF is characterized by a sudden worsening of symptoms in patients with pre-existing heart failure. This can be triggered by factors such as infections, medication non-compliance, or other stressors on the heart. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further complications.
Causes
The causes of Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF can vary, but common triggers include infections, excessive salt intake, uncontrolled hypertension, and arrhythmias. These factors can place additional strain on the heart, leading to a worsening of symptoms and a need for urgent medical intervention.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF may include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs and abdomen, coughing, and rapid weight gain. Patients may also experience chest pain, dizziness, and confusion. These symptoms can be indicative of a worsening heart condition and should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF is typically made based on a combination of symptoms, physical exam findings, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, chest X-ray, and blood tests to assess heart function and detect any underlying causes of the exacerbation.
Treatment
Treatment for Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF aims to stabilize the patient, relieve symptoms, and improve heart function. This may involve medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and inotropes. Lifestyle modifications, such as a low-salt diet and regular exercise, may also be recommended to manage this condition.
Conclusion
Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent further complications. Accurate coding and documentation of this condition are essential for proper management and reimbursement. Healthcare providers should stay informed of the latest coding guidelines and updates to ensure the best care for patients with this condition.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between acute and chronic heart failure?
Acute heart failure refers to a sudden onset of symptoms, while chronic heart failure is a long-term condition that worsens over time.
2. Can Acute on Chronic Systolic CHF be reversed?