Adenocarcinoma Of The Esophagus: ICD-10 Overview And Diagnosis Codes
What is Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus ICD-10?
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. ICD-10 is the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, a system used by healthcare providers to classify and code diseases, symptoms, and medical procedures for billing and record-keeping purposes.
Code Information for Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus ICD-10
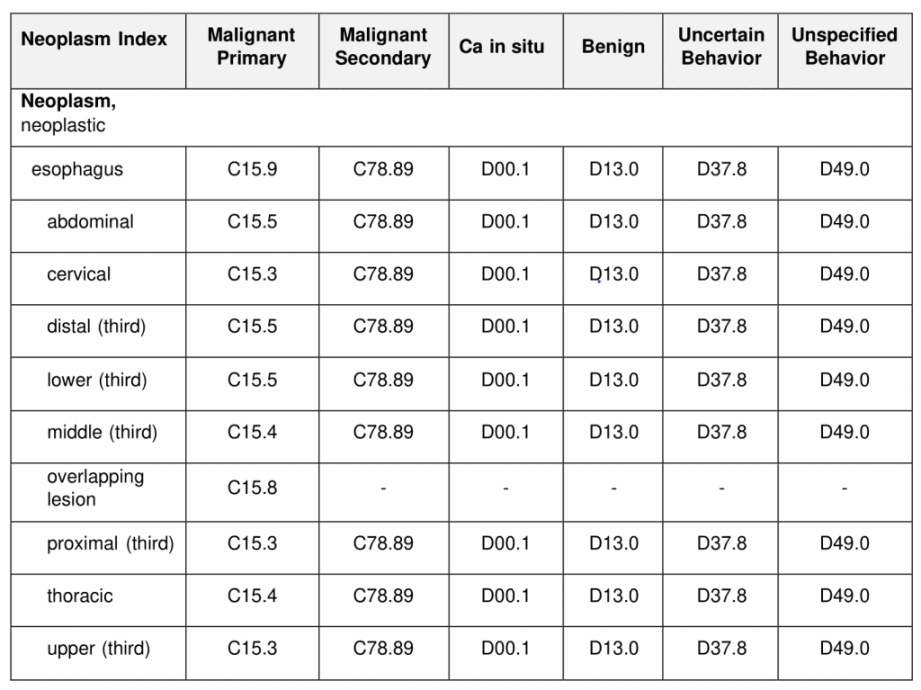
The ICD-10 code for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is C15.5. This code is used to specify the type and location of the cancer when documenting medical records and submitting insurance claims.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG) for Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus
The MS-DRG for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is 138. This DRG is used to categorize patients with similar diagnoses who require similar treatments for the purpose of reimbursement by Medicare and other health insurance providers.
Convert to ICD-9 Code for Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus
The ICD-9 code for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is 150.5. This code was used prior to the implementation of the ICD-10 system and may still be referenced in some medical records and databases.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus was first introduced in 2015 as part of the tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases. This update provided more specific codes for various types of cancer, including adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used interchangeably with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus include esophageal adenocarcinoma, esophageal cancer, and adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction. These terms all refer to the same type of cancer affecting the esophagus.
Clinical Information
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus typically begins in the cells of the glandular tissue that line the esophagus. This type of cancer is more common in men than women and is often associated with risk factors such as obesity, smoking, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Causes of Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus
The exact cause of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is not known, but certain factors have been linked to an increased risk of developing this type of cancer. These risk factors include chronic acid reflux, obesity, smoking, and a diet high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables.
Symptoms of Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus
Common symptoms of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus may include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, weight loss, and coughing or hoarseness. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the stage of the cancer and the extent of tumor growth.
Diagnosis of Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus
Diagnosing adenocarcinoma of the esophagus typically involves a combination of imaging tests such as endoscopy, biopsy, and imaging scans like CT or MRI. These tests help determine the location, size, and extent of the cancer to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus
Treatment for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and other individual factors.
Conclusion
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is a type of cancer that affects the cells of the esophagus and is classified using the ICD-10 code C15.5. This cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of imaging tests and biopsies, and treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Knowing the symptoms and risk factors associated with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus can help individuals seek early detection and appropriate treatment.