Dilated Aortic Root: An ICD-10 Overview
What is Aortic Root Dilated ICD 10?
Aortic root dilated ICD 10 is a medical condition that is classified under the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) coding system. It is a condition where the aortic root, which is the section of the aorta closest to the heart, becomes enlarged and stretched beyond its normal size. This can lead to various complications and health issues if left untreated.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for aortic root dilated is I28.1. This code is used by healthcare providers to accurately diagnose and document cases of aortic root dilation in patients. By using the correct ICD-10 code, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients receive the appropriate care and treatment for their condition.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
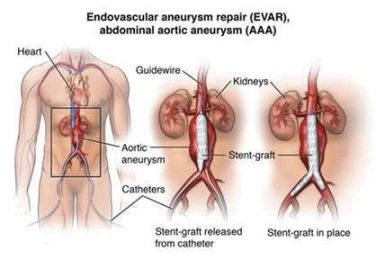
Patients with aortic root dilation may be grouped under specific Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG) for billing and reimbursement purposes. The exact MS-DRG may vary depending on the severity of the condition and any associated complications. Healthcare providers can use these groupings to streamline the billing process and ensure that patients receive the proper level of care.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
Prior to the implementation of the ICD-10 coding system, aortic root dilation was classified under the ICD-9 code 441.7. While the transition to ICD-10 has provided more detailed and specific codes, healthcare providers may still encounter cases where they need to convert ICD-10 codes back to ICD-9 for certain purposes.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for aortic root dilation, I28.1, was first introduced in 2016 as part of the regular updates and revisions to the coding system. This new code allowed for more accurate documentation and tracking of cases of aortic root dilation, leading to improved patient care and outcomes.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for aortic root dilation include aortic root aneurysm, aortic root enlargement, and aortic root dilatation. These terms may be used interchangeably with aortic root dilation in medical literature and discussions, but they all refer to the same underlying condition.
Clinical Information
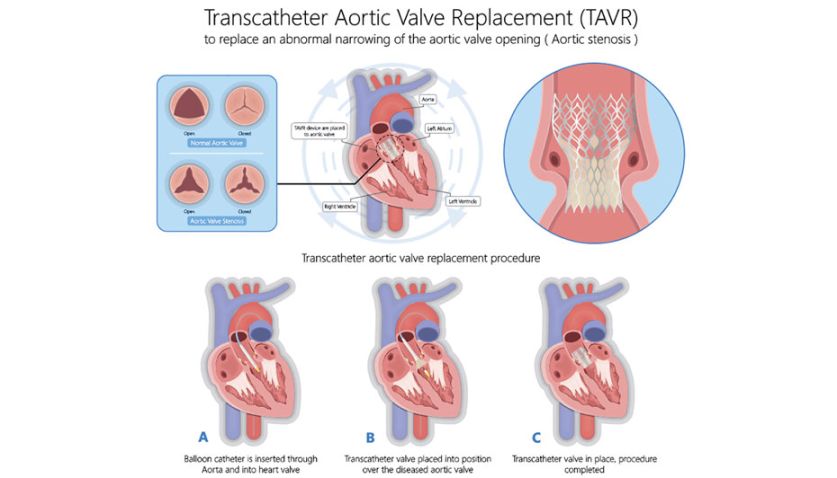
Aortic root dilation can be a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. It is often associated with underlying cardiovascular disorders such as Marfan syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, and aortic dissection. Patients with aortic root dilation may be at increased risk for complications such as aortic rupture, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death.
Causes
The exact cause of aortic root dilation is not always clear, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In some cases, aortic root dilation may be hereditary and run in families. Other possible causes include high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and connective tissue disorders.
Symptoms

Patients with aortic root dilation may not always experience symptoms, especially in the early stages of the condition. However, as the aortic root enlarges, patients may start to experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue. In severe cases, symptoms may indicate a life-threatening complication such as aortic dissection.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing aortic root dilation typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Healthcare providers may use echocardiography, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the aortic root and assess its size and shape. Blood tests may also be performed to rule out underlying conditions.
Treatment
The treatment for aortic root dilation depends on the underlying cause, severity of the condition, and presence of symptoms. In some cases, monitoring the condition with regular imaging tests may be sufficient. However, if the aortic root is significantly enlarged or at risk of complications, surgical intervention such as aortic root replacement may be necessary.
Conclusion
Aortic root dilation is a serious medical condition that requires accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By using the ICD-10 code I28.1, healthcare providers can ensure that patients with aortic root dilation receive the necessary care and monitoring to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
FAQs
1. Is aortic root dilation a common condition?
Aortic root dilation is relatively uncommon