The Challenge Of Diagnosing Anemia In Chronic Kidney Disease: ICD-10 Coding And Management Strategies
What is Anemia Chronic Kidney Disease ICD 10?
Anemia chronic kidney disease ICD 10 is a medical condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells in the body due to impaired kidney function. The kidneys play a crucial role in the production of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, they are unable to produce enough erythropoietin, leading to a decrease in red blood cell production and ultimately anemia.
Code Information
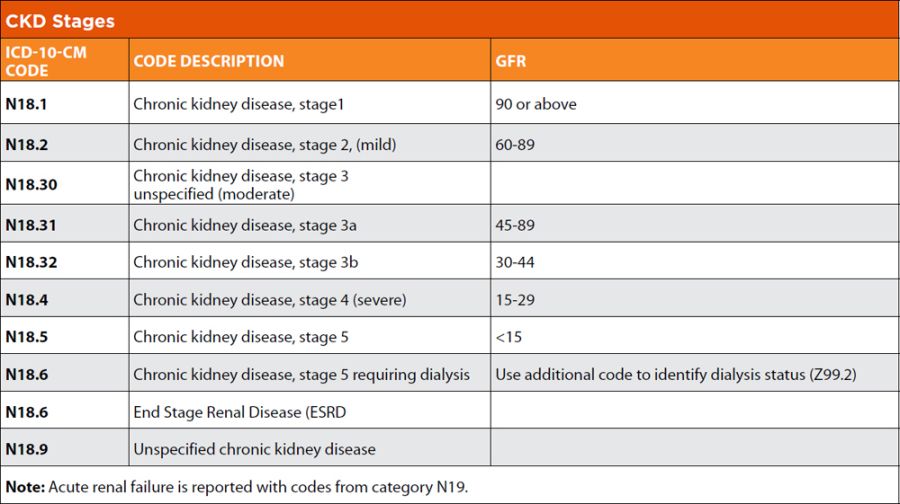
The ICD-10 code for anemia chronic kidney disease is N18.81. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

Patients with anemia chronic kidney disease may fall under the MS-DRG 682 – Renal Failure with Major Complications or Comorbidities. This DRG is used to classify patients with chronic kidney disease who require treatment for complications such as anemia.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

For those familiar with ICD-9 coding, the equivalent code for anemia chronic kidney disease in ICD-9 is 285.21.
Code History
The ICD-10 code N18.81 for anemia chronic kidney disease was implemented in October 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used to describe anemia in chronic kidney disease include renal anemia, anemia of renal origin, and anemia secondary to chronic kidney disease.
Clinical Information
Anemia in chronic kidney disease is a common complication that can significantly impact the quality of life and overall health of patients. It is important to monitor and manage anemia in these patients to prevent complications such as fatigue, weakness, and cardiovascular disease.
Causes
The primary cause of anemia in chronic kidney disease is the impaired production of erythropoietin by the kidneys. Other contributing factors may include iron deficiency, inflammation, and bone marrow suppression.
Symptoms
Symptoms of anemia in chronic kidney disease may include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin, and dizziness. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the degree of anemia.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of anemia in chronic kidney disease is typically made through blood tests that measure hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Additional tests may be ordered to determine the underlying cause of the anemia, such as iron studies and erythropoietin levels.
Treatment
Treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease may include erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to stimulate red blood cell production, iron supplementation to address iron deficiency, and blood transfusions in severe cases. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion
Overall, anemia in chronic kidney disease is a common complication that requires careful monitoring and management to prevent complications and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition, patients can take steps to better manage their health and well-being.
FAQs:
1. How common is anemia in chronic kidney disease?
2. What are the risk factors for developing anemia in chronic kidney disease?
3. What are the potential complications of untreated anemia in chronic kidney disease?
4. Can anemia in chronic kidney disease be cured?
5. How often should patients with anemia in chronic kidney disease be monitored by a healthcare provider?