Impact Of ICD-10 Narcolepsy Without Cataplexy On Diagnosis And Treatment
What is Narcolepsy Without Cataplexy?
Narcolepsy without cataplexy, also known as type 2 narcolepsy, is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden episodes of sleep, and disrupted nighttime sleep patterns. Unlike narcolepsy with cataplexy, individuals with narcolepsy without cataplexy do not experience sudden muscle weakness or loss of muscle control (cataplexy).
Code Information

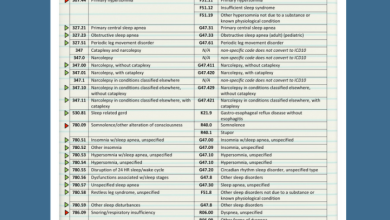
ICD-10 Code: G47.411
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

MS-DRG: 101-103
Convert to ICD-9 Code

ICD-9 Code: 347.01
Code History
The ICD-10 code for narcolepsy without cataplexy was introduced in 2011 to provide a more specific diagnosis for healthcare providers and researchers.
Approximate Synonyms
Narcolepsy type 2
Hypersomnia with sleep apnea
Clinical Information
Narcolepsy without cataplexy is believed to be caused by a deficiency of hypocretin, a neuropeptide that regulates wakefulness and REM sleep. This deficiency can result in abnormal sleep patterns and excessive daytime sleepiness.
Causes
The exact cause of narcolepsy without cataplexy is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors. In some cases, the condition may be triggered by a viral infection or head injury.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of narcolepsy without cataplexy include excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden episodes of sleep, sleep paralysis, and hallucinations upon falling asleep or waking up. Other symptoms may include fragmented nighttime sleep, automatic behaviors, and cognitive difficulties.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing narcolepsy without cataplexy often involves a comprehensive evaluation by a sleep specialist, including a physical exam, medical history, sleep diary, sleep study (polysomnography), and multiple sleep latency test (MSLT). Blood tests may also be conducted to measure hypocretin levels.
Treatment
Treatment for narcolepsy without cataplexy typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and behavioral therapy. Medications such as stimulants, antidepressants, and sodium oxybate may be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve wakefulness and nighttime sleep quality.
Conclusion
Narcolepsy without cataplexy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, disrupted nighttime sleep patterns, and sudden episodes of sleep. While the exact cause of the condition is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors. Diagnosis and treatment typically involve a comprehensive evaluation by a sleep specialist and may include medications, lifestyle modifications, and behavioral therapy.
FAQs
1. Can narcolepsy without cataplexy be cured?
2. What are the long-term effects of narcolepsy without cataplexy?
3. Is narcolepsy without cataplexy a genetic condition?
4. How is narcolepsy without cataplexy diagnosed?
5. Can lifestyle changes help manage narcolepsy without cataplexy symptoms?