Understanding Anemia In Chronic Kidney Disease: A Guide To ICD-10 Coding
What is Anemia in CKD ICD-10?
Anemia in CKD ICD-10 refers to the condition of having low levels of red blood cells in the body due to chronic kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive condition where the kidneys are unable to function properly, leading to a buildup of waste and fluids in the body. Anemia is a common complication of CKD and can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life.
Code Information

The ICD-10 code for anemia in CKD is N18.8. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. It is important for healthcare providers to accurately document and code this condition to ensure proper reimbursement and tracking of the patient’s health status.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
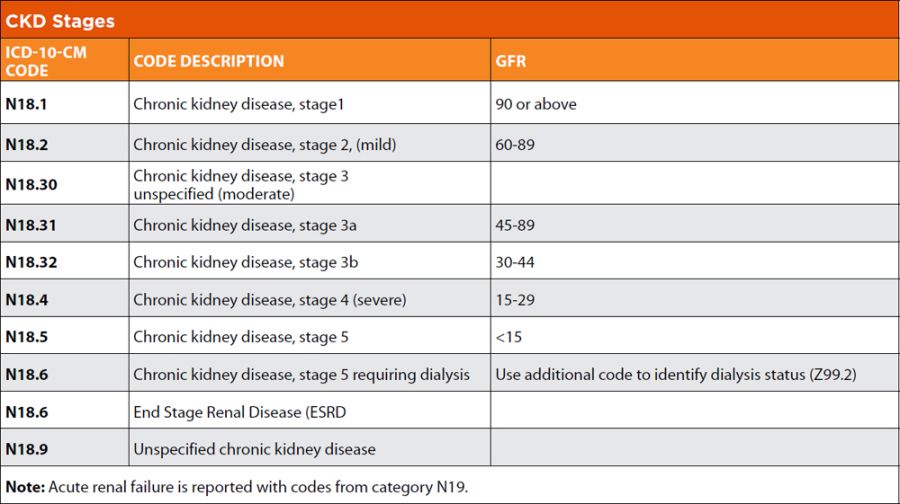
The MS-DRG for anemia in CKD is MS-DRG 682. This DRG is used to classify and group patients with similar diagnoses and treatments for reimbursement purposes. Patients with anemia in CKD may fall under this DRG when admitted to a hospital for treatment.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
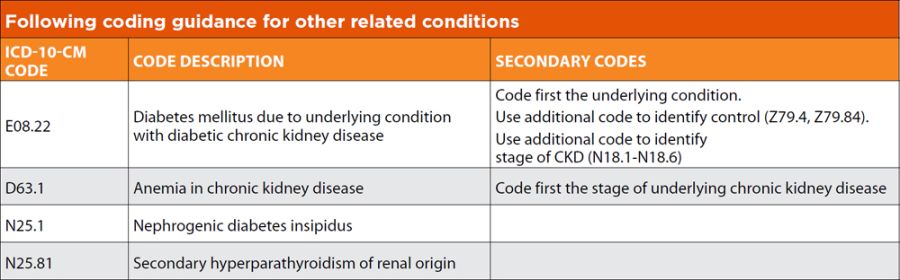
The ICD-10 code N18.8 for anemia in CKD can be converted to the ICD-9 code 585.9. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to chronic kidney disease and can help healthcare providers track and manage the condition in patients.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for anemia in CKD was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 code sets. This change was made to improve the accuracy and specificity of coding for various medical conditions, including anemia in CKD.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for anemia in CKD include renal anemia, kidney disease anemia, and chronic renal failure anemia. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe the same condition of low red blood cell levels in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Clinical Information
Anemia in CKD is a common complication of chronic kidney disease and is often caused by the decreased production of erythropoietin, a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production. This results in a decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Causes
The main cause of anemia in CKD is the progressive loss of kidney function, which leads to a decrease in erythropoietin production. Other factors that can contribute to anemia in CKD include iron deficiency, inflammation, and blood loss. Treatment for anemia in CKD often involves addressing these underlying causes to improve red blood cell production and levels.
Symptoms
Symptoms of anemia in CKD can vary from mild to severe and may include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness, and chest pain. These symptoms can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life and may require medical intervention to manage effectively.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing anemia in CKD typically involves a combination of blood tests, physical exams, and medical history review. Blood tests such as hemoglobin levels, hematocrit levels, and iron studies are used to confirm the presence of anemia and determine its severity. Healthcare providers may also perform additional tests to identify underlying causes of anemia, such as iron deficiency or inflammation.
Treatment
Treatment for anemia in CKD aims to improve red blood cell production and levels to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. This may involve medications such as erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to stimulate red blood cell production, iron supplements to correct iron deficiency, and blood transfusions in severe cases. In some instances, patients may also require additional treatments such as dialysis or kidney transplant to improve kidney function and manage anemia effectively.
Conclusion
Anemia in CKD is a common complication of chronic kidney disease that can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage anemia effectively and improve the patient’s overall health. Healthcare providers should be aware of the ICD-10 code N18.8 for anemia in CKD to accurately code and document this condition for reimbursement and tracking purposes.