ICD-10 Code For Aortic Root Dilatation: I71.01
What is Aortic Root Dilatation ICD 10?
Aortic root dilatation ICD 10 is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement or bulging of the aortic root, which is the beginning portion of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. This condition can lead to serious complications if left untreated, including aortic dissection, aneurysm, and heart valve problems.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for aortic root dilatation is I77.9. This code is used to classify and report the condition in medical records and billing purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
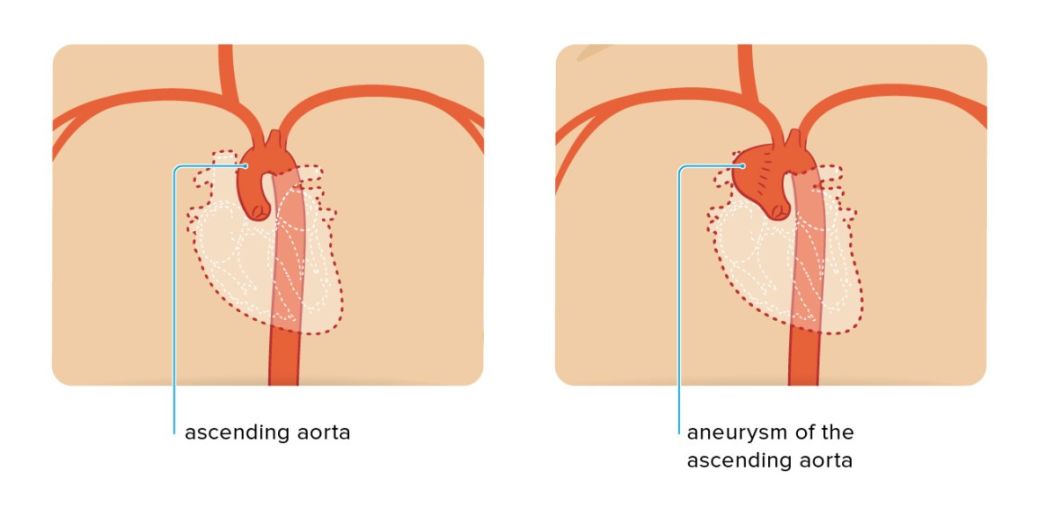
For patients with aortic root dilatation, the MS-DRG is 309 – Cardiac Arrhythmia and Conduction Disorders with CC/MCC. This grouping is used for reimbursement purposes for inpatient hospital stays.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
In the ICD-9 coding system, aortic root dilatation is classified under code 441.9 – Aortic Aneurysm of unspecified site. This code is used to document the condition in medical records.
Code History
The I77.9 code for aortic root dilatation was introduced in the ICD-10 coding system, which replaced the older ICD-9 system. This change was made to provide more specific and detailed codes for medical conditions.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for aortic root dilatation include aortic root aneurysm, aortic root enlargement, and aortic root bulge. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the condition.
Clinical Information

Aortic root dilatation is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making it difficult to diagnose. However, as the condition progresses, patients may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations. Diagnosis is typically confirmed through imaging tests such as echocardiography and CT scans.
Causes
The main cause of aortic root dilatation is thought to be genetic factors, as it tends to run in families. Other risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, and connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome.
Symptoms
Symptoms of aortic root dilatation can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations. In some cases, the condition may be asymptomatic until complications arise.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing aortic root dilatation typically involves a physical exam, medical history review, and imaging tests such as echocardiography, CT scans, and MRI. Blood tests may also be conducted to check for signs of inflammation or infection.
Treatment
Treatment for aortic root dilatation depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of symptoms. In mild cases, close monitoring may be recommended, while more severe cases may require surgical intervention to repair or replace the enlarged aortic root.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aortic root dilatation ICD 10 is a serious medical condition that can lead to potentially life-threatening complications if left untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential in managing the condition and preventing further complications. It is important for individuals with a family history of aortic root dilatation or risk factors to undergo regular screening and follow-up with a healthcare provider.
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for aortic root dilatation?
Common risk factors for aortic root dilatation include genetic factors, high blood pressure, smoking, and connective tissue disorders.
2. Can aortic root dilatation be prevented?
While the condition may be hereditary, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure, and avoiding smoking can help reduce the risk of developing aortic root dilatation.
3. How is aortic root dilatation diagnosed?
Diagnosis of aortic root dilatation typically involves a physical exam, imaging tests such as echocardiography, CT scans, and MRI, and blood tests.
4. What are the treatment options for aortic root dilatation?
Treatment for aortic root dilatation may include