Battling Bullous Pemphigoid: Understanding The ICD-10 Code And Treatment Options
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
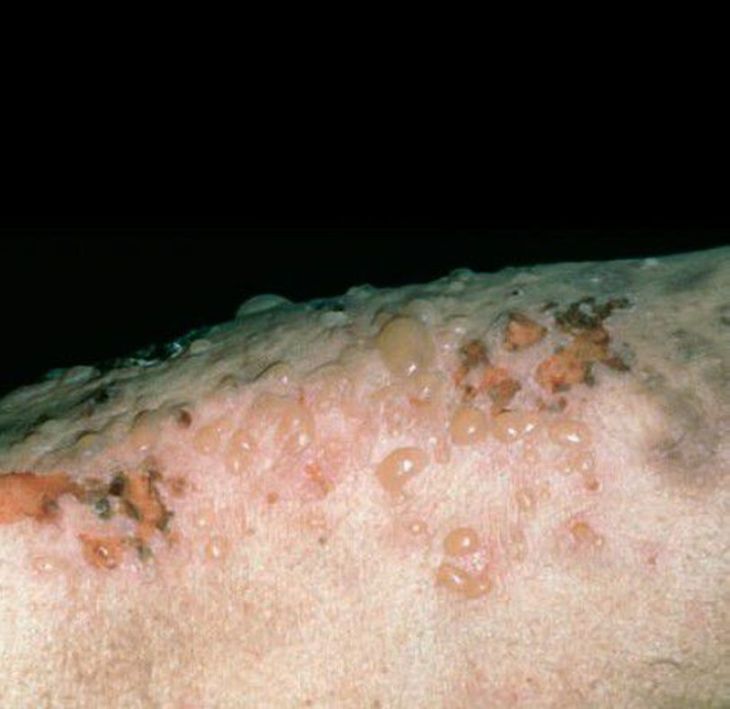
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin disorder that causes large, fluid-filled blisters to form on the skin. It is characterized by the immune system attacking the layer of skin below the outer layer, leading to the formation of blisters. The blisters can be painful and itchy, and can occur anywhere on the body.
Code Information
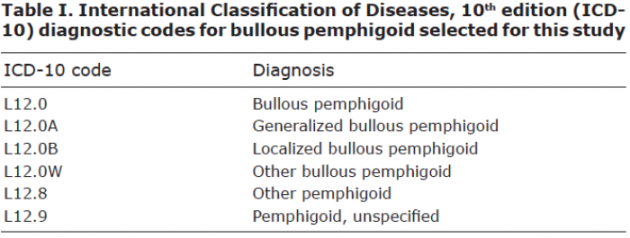
The ICD-10 code for bullous pemphigoid is L12.0.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
The MS-DRG for bullous pemphigoid is DRG 606 – Minor skin disorders with MCC (Major Complications or Comorbidities) or skin graft.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The ICD-9 code for bullous pemphigoid is 694.5.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for bullous pemphigoid was introduced in 2015, replacing the previous ICD-9 code.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for bullous pemphigoid include benign pemphigus, chronic bullous dermatosis, and pemphigoid.
Clinical Information
Bullous pemphigoid is more common in elderly individuals, typically occurring in those over the age of 60. It is caused by an immune system dysfunction that leads to the production of antibodies that attack the skin. The exact cause of this immune system dysfunction is unknown.
Causes
The exact cause of bullous pemphigoid is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a malfunction in the immune system that leads to the production of antibodies that attack the skin. Certain factors, such as genetics and environmental triggers, may play a role in the development of the condition.
Symptoms
The main symptom of bullous pemphigoid is the presence of large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. These blisters can be painful, itchy, and may rupture, leading to open sores. Other symptoms may include red, inflamed skin, and skin that is easily irritated.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid is typically made through a physical examination of the skin and a biopsy of the affected area. Blood tests may also be performed to check for the presence of antibodies that are associated with the condition.
Treatment
Treatment for bullous pemphigoid aims to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent the formation of new blisters. This may include the use of corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and immunosuppressants to suppress the immune system. Topical treatments, such as creams and ointments, may also be used to help relieve symptoms and promote healing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin disorder that causes large, fluid-filled blisters to form on the skin. It is more common in elderly individuals and is caused by an immune system dysfunction. Treatment typically involves reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms through the use of medications and topical treatments.
FAQs
1. Is bullous pemphigoid a common skin disorder?
2. What is the main symptom of bullous pemphigoid?
3. How is bullous pemphigoid diagnosed?
4. Can bullous pemphigoid be cured?
5. Are there any risk factors for developing bullous pemphigoid?