Understanding Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia: Exploring ICD-10 Codes And Diagnosis
What is Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia (CLL) ICD 10?
Chronic lymphoid leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that starts from white blood cells (lymphocytes) in the bone marrow. It is a slow-growing cancer that mainly affects older adults. In the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), CLL is classified under the code C91.1.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for chronic lymphoid leukemia is C91.1. It falls under the category of Malignant neoplasm of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
CLL is classified under the MS-DRG 017 – Myeloproliferative Disorders or Poorly Differentiated Neoplasms with Major O.R. Procedure with CC/MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for chronic lymphoid leukemia is 204.1.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for CLL was introduced in October 2015 as part of the tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used interchangeably with chronic lymphoid leukemia include B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic leukemia, and hairy cell leukemia.
Clinical Information
CLL is a type of leukemia that primarily affects B-cell lymphocytes. The cancerous cells accumulate in the bone marrow and interfere with the production of normal blood cells. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and frequent infections.
Causes
The exact cause of CLL is unknown, but certain risk factors have been identified, including older age, family history of CLL, and exposure to certain chemicals such as benzene.
Symptoms
The symptoms of CLL can vary from person to person but may include enlarged lymph nodes, fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, and frequent infections.
Diagnosis
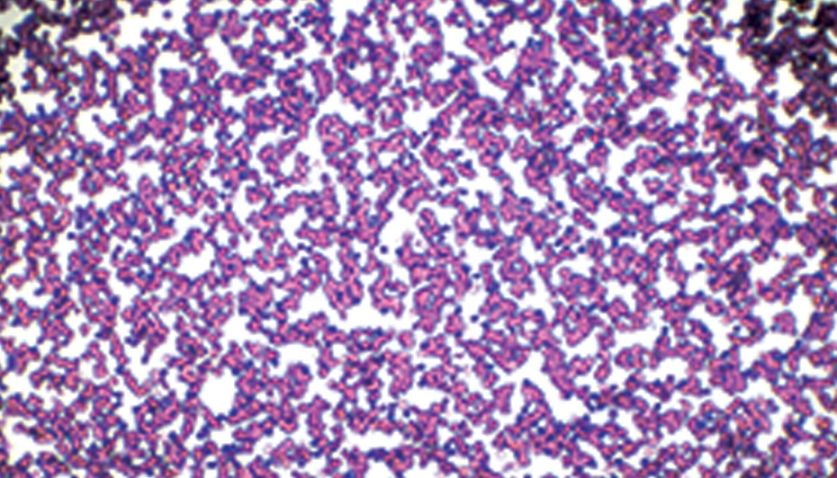
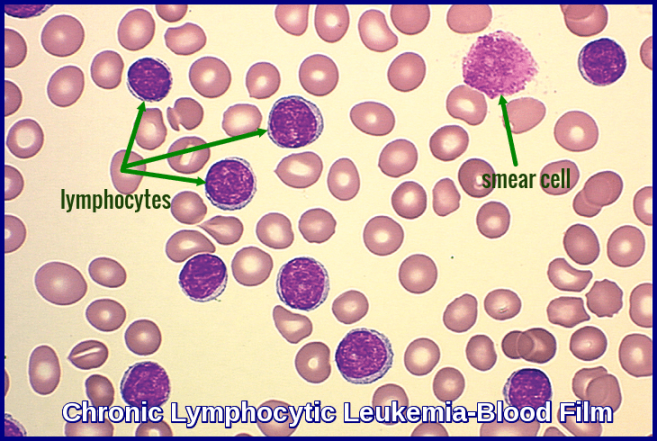
CLL is usually diagnosed through blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs. The presence of abnormal lymphocytes in the blood or bone marrow is a key indicator of CLL.
Treatment
Treatment for CLL depends on the stage of the disease and may include watchful waiting, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplant.
Conclusion
Chronic lymphoid leukemia is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells and is classified under the ICD-10 code C91.1. It is a slow-growing cancer that primarily affects older adults and can be diagnosed through blood tests and imaging studies. Treatment options for CLL include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplant.
FAQs
1. Can chronic lymphoid leukemia be cured?
2. What are the risk factors for developing CLL?
3. How is CLL diagnosed?
4. What are the treatment options for CLL?
5. What is the prognosis for patients with CLL?