Understanding ICD-10 Coding For Bronchial Asthma: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Bronchial Asthma?
Bronchial asthma, commonly known as asthma, is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. This inflammation leads to difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and tightness in the chest. Asthma symptoms can range from mild to severe and can be triggered by various factors such as allergens, exercise, cold air, pollutants, and stress.
Code Information
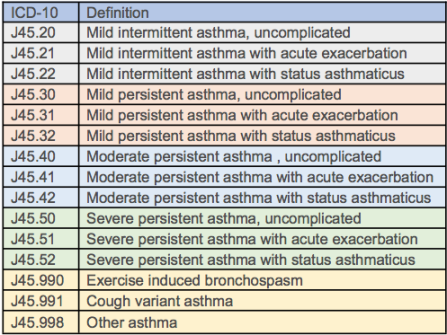
The ICD-10 code for bronchial asthma is J45. J45 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. It is important to assign the correct ICD-10 code for accurate medical coding and billing.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
The Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Group (MS-DRG) for bronchial asthma is MS-DRG 196. This DRG is used to classify patients with similar clinical characteristics and determine the reimbursement for their hospital stay related to bronchial asthma.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for bronchial asthma is 493. This code was used prior to the implementation of ICD-10 and is no longer in use for medical coding purposes.
Code History
The ICD-10 code J45 for bronchial asthma was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding system. This new coding system provides more specificity and accuracy in coding diagnoses related to bronchial asthma.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used as approximate synonyms for bronchial asthma include bronchial hyperreactivity, reactive airway disease, and allergic bronchitis. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe the same condition of asthma.
Clinical Information
Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes recurring episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing. These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency and may be triggered by various factors such as allergens, exercise, infections, and stress.
Causes
The exact cause of bronchial asthma is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Common triggers for asthma symptoms include allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, respiratory infections, air pollution, smoke, cold air, exercise, and stress.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bronchial asthma can vary from person to person and may include wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may worsen during asthma attacks triggered by various factors.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing bronchial asthma involves a physical examination, medical history review, lung function tests such as spirometry, and allergy testing. Doctors may also use imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans to rule out other respiratory conditions that may mimic asthma symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment for bronchial asthma aims to control symptoms, prevent asthma attacks, and improve lung function. Common treatment options include inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, leukotriene modifiers, and immunotherapy. It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized asthma management plan.
Conclusion
Bronchial asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential in managing asthma symptoms and improving quality of life for patients. By understanding the ICD-10 code for bronchial asthma and its clinical implications, healthcare providers can effectively code, bill, and treat patients with this condition.
FAQs
1. What are the common triggers for bronchial asthma?
Common triggers for bronchial asthma include allergens, exercise, infections, air pollution, smoke, cold air, and stress.
2. How is bronchial asthma diagnosed?
Bronchial asthma is diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history review, lung function tests, and allergy testing.
3. What are the treatment options for bronchial asthma?