Understanding ICD-10 Codes For Mitral Valve Regurgitation
What is ICD 10 Mitral Valve Regurgitation?
ICD 10 Mitral Valve Regurgitation refers to a condition where the mitral valve in the heart does not close tightly, causing blood to flow backward into the heart. This can lead to various symptoms and complications, affecting the overall function of the heart.
Code Information
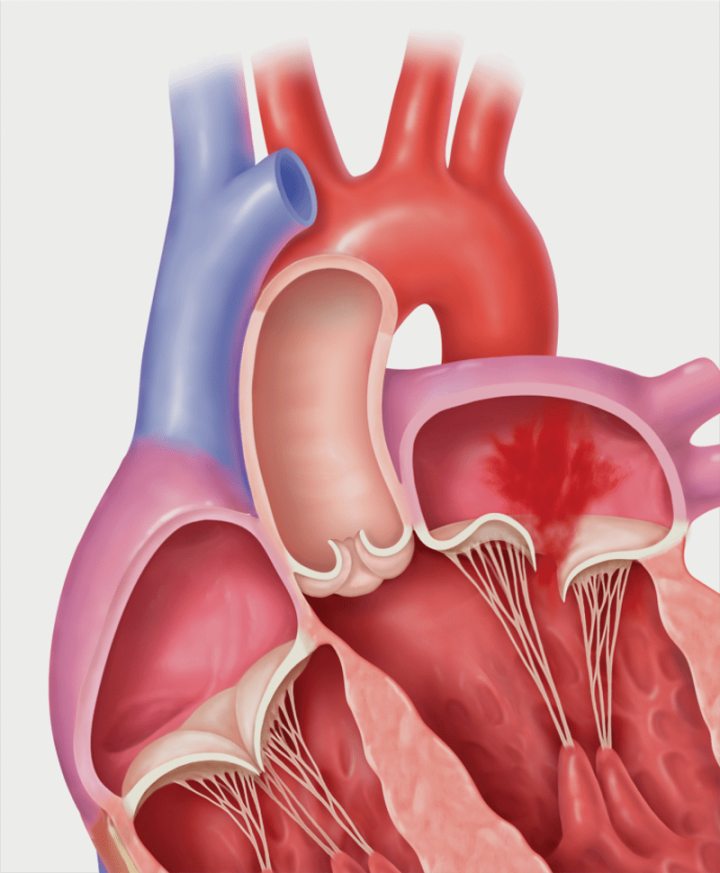
The ICD 10 code for Mitral Valve Regurgitation is I34.1. This code is used to classify and track cases of mitral valve regurgitation in medical records and databases.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
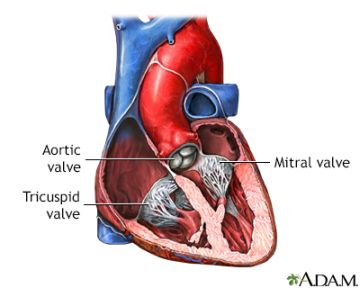
When it comes to reimbursement and classification of medical procedures related to mitral valve regurgitation, it falls under MS-DRG 228 – Other Cardiothoracic Procedures with MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
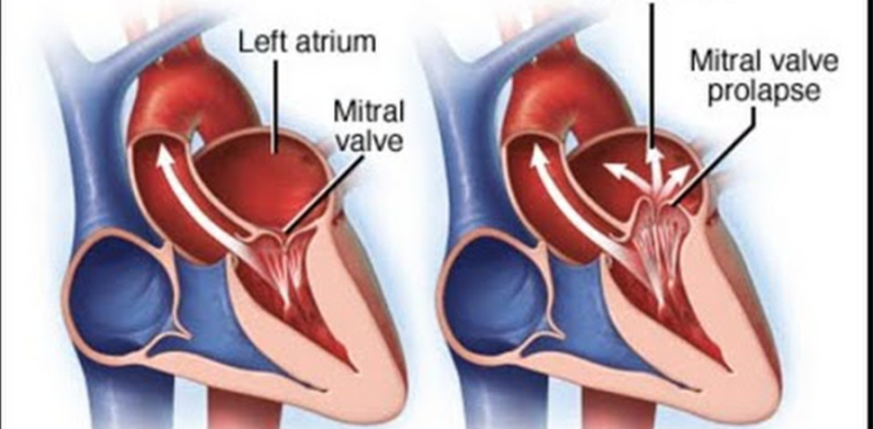
In the previous coding system, the ICD-9 code for Mitral Valve Regurgitation was 424.0. However, with the transition to ICD-10, the code I34.1 is now used for this condition.
Code History

The ICD-10 code I34.1 for Mitral Valve Regurgitation was introduced in October 2015 as part of the regular updates to the coding system to improve accuracy and specificity in coding medical conditions.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used interchangeably with Mitral Valve Regurgitation include Mitral Insufficiency, Mitral Regurgitation, and Mitral Valve Incompetence.
Clinical Information
Mitral Valve Regurgitation can be classified as either acute or chronic, depending on the duration and severity of the condition. Acute cases may be caused by conditions such as infective endocarditis or myocardial infarction, while chronic cases are often associated with degenerative changes in the mitral valve.
Causes
There are several potential causes of Mitral Valve Regurgitation, including congenital heart defects, rheumatic heart disease, mitral valve prolapse, and heart attacks. Other factors such as age, genetics, and certain medications may also contribute to the development of the condition.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Mitral Valve Regurgitation may include fatigue, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, chest pain, and swelling in the legs and feet. In severe cases, the condition can lead to heart failure and other serious complications.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Mitral Valve Regurgitation typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests such as echocardiography, and possibly a cardiac catheterization procedure to assess the severity of the regurgitation and its impact on heart function.
Treatment
Treatment options for Mitral Valve Regurgitation may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the presence of any underlying heart conditions. In some cases, medication therapy may help manage symptoms, while surgical interventions such as valve repair or replacement may be necessary to correct the regurgitation and improve heart function.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ICD 10 Mitral Valve Regurgitation is a serious heart condition that can have significant implications for overall health and well-being. Proper diagnosis and management of the condition are essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life for affected individuals.
FAQs
What are the risk factors for developing Mitral Valve Regurgitation?
How is Mitral Valve Regurgitation treated?
Can Mitral Valve Regurgitation be prevented?
What are the long-term outcomes for individuals with Mitral Valve Regurgitation?
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Mitral Valve Regurgitation?