Navigating Bullous Pemphigoid In ICD-10
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin disorder that causes blistering and inflammation of the skin. It is characterized by the development of large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin that can be painful and itchy. Bullous pemphigoid is more common in older adults, typically those over the age of 60, but it can affect people of any age.
Code Information

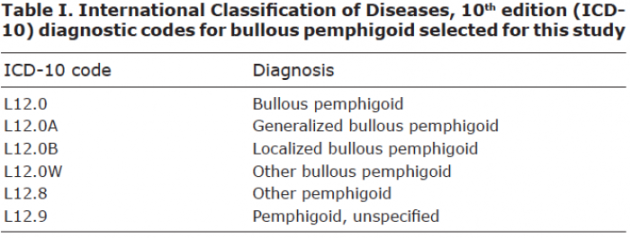
The ICD-10 code for bullous pemphigoid is L12.0. This code is used to classify and code for the condition in medical billing and coding systems. It is important for accurate documentation and reimbursement purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Bullous pemphigoid falls under MS-DRG 606, which includes skin grafts and wound debridement for skin ulcers. This DRG is used to classify patients with similar diagnoses and treatment procedures for billing and reimbursement purposes.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
In the ICD-9 coding system, bullous pemphigoid is classified under code 694.5. This code is used to document and classify the condition for billing and coding purposes.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for bullous pemphigoid was introduced in October 2015 as part of the ICD-10-CM code set. It replaced the previous ICD-9 code 694.5 for the condition.
Approximate Synonyms
Bullous pemphigoid
Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis
Benign pemphigoid
Clinical Information
Bullous pemphigoid is caused by a malfunction in the immune system, where antibodies mistakenly attack the skin and cause inflammation. This leads to the formation of blisters on the skin, which can be triggered by certain medications, infections, or other underlying health conditions.
Causes
The exact cause of bullous pemphigoid is unknown, but it is believed to be triggered by an autoimmune response where the immune system attacks the skin. Certain medications, infections, and genetic factors may also play a role in the development of the condition.
Symptoms
The main symptom of bullous pemphigoid is the presence of large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin that can be painful and itchy. Other symptoms may include redness, swelling, and inflammation of the skin, as well as skin lesions and itchiness.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing bullous pemphigoid typically involves a physical examination of the skin, as well as a skin biopsy to confirm the presence of the condition. Blood tests may also be conducted to check for specific antibodies associated with the disease.
Treatment
Treatment for bullous pemphigoid usually involves the use of corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. Other medications, such as immunosuppressants and antibiotics, may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin disorder characterized by the development of large blisters on the skin. It is important to accurately code and document the condition using the ICD-10 code L12.0 for billing and reimbursement purposes. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with bullous pemphigoid.
FAQs
1. Can bullous pemphigoid be cured?
2. Is bullous pemphigoid contagious?
3. What are the risk factors for developing bullous pemphigoid?
4. How is bullous pemphigoid different from other skin conditions?
5. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage bullous pemphigoid symptoms?