Utilizing ICD-10 Screening Codes For Hepatitis C Detection
What is ICD-10 Screening for Hepatitis C?
ICD-10 screening for hepatitis C is a diagnostic code used in the healthcare industry to identify patients who are at risk for or have been diagnosed with hepatitis C. Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation, sometimes leading to serious liver damage. Screening for hepatitis C is important for early detection and treatment to prevent complications.
Code Information
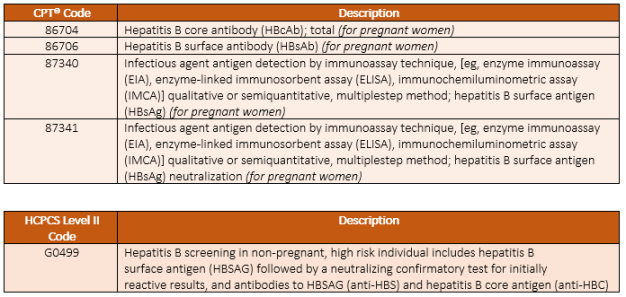
The ICD-10 code for screening for hepatitis C is Z11.3. This code is used to indicate that a patient is being screened for hepatitis C, whether they are at high risk or have symptoms that warrant testing. The Z11.3 code is important for tracking and monitoring the prevalence of hepatitis C in populations.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
There is no specific MS-DRG related to screening for hepatitis C. However, patients who are diagnosed with hepatitis C may be assigned a different DRG based on the severity of their condition and the treatments required.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for screening for hepatitis C is V73.89. This code is used to indicate screening for other specified viral diseases, including hepatitis C.
Code History
The ICD-10 code Z11.3 for screening for hepatitis C was introduced in October 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems. This change allowed for more specific coding of healthcare services related to hepatitis C screening.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for screening for hepatitis C include testing for HCV, hepatitis C antibody test, and HCV screening.
Clinical Information
Hepatitis C is a bloodborne virus that primarily affects the liver, causing inflammation and potentially leading to liver cirrhosis or cancer. Screening for hepatitis C involves testing for the presence of the virus in the blood through antibody and viral load tests.
Causes
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which is most commonly spread through blood-to-blood contact. This can occur through sharing needles, receiving contaminated blood transfusions, or having unprotected sex with an infected person.
Symptoms
Many people with hepatitis C do not experience any symptoms, especially in the early stages of the infection. However, some common symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, jaundice, and abdominal pain.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hepatitis C involves a series of blood tests to detect the presence of the virus and assess liver function. These tests may include antibody tests, viral load tests, and liver enzyme tests.
Treatment
Treatment for hepatitis C typically involves antiviral medications to reduce the viral load and prevent liver damage. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary for patients with advanced liver disease.
Conclusion
ICD-10 screening for hepatitis C is a crucial component of healthcare management for patients at risk for or diagnosed with hepatitis C. Early detection and treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes for patients with hepatitis C.
FAQs
1. How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is most commonly transmitted through blood-to-blood contact, such as sharing needles or receiving contaminated blood transfusions.
2. What are the symptoms of hepatitis C?
Symptoms of hepatitis C may include fatigue, nausea, jaundice, and abdominal pain, although many people with the infection may not experience any symptoms.
3. How is hepatitis C diagnosed?
Diagnosis of hepatitis C involves blood tests to detect the presence of the virus and assess liver function.
4. What is the treatment for hepatitis C?
Treatment for hepatitis C typically involves antiviral medications to reduce the viral load and prevent liver damage.
5. Why is screening for hepatitis C important?
Screening for hepatitis C is important for early detection and treatment to prevent complications and improve outcomes for patients with the infection.