Understanding The ICD-10 Codes For Screening Hepatitis C
What is ICD-10 for Screening Hepatitis C?
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. It is a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO) that codes various diseases and health conditions. In this article, we will focus on the ICD-10 code for screening hepatitis C.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for screening hepatitis C is Z11.3. This code is used when a patient undergoes a screening test for hepatitis C, even if the test results are negative. It is important to use this code for proper documentation and billing purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

There is no specific MS-DRG related to screening hepatitis C as it is a preventive measure rather than a treatment for an existing condition. However, healthcare facilities may still use the ICD-10 code Z11.3 for reimbursement and tracking purposes.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
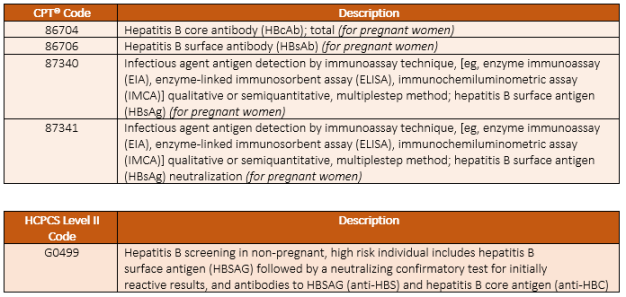
In the previous ICD-9 coding system, screening for hepatitis C was coded under V73.89. If you are converting ICD-10 codes to ICD-9, you would use this code for screening hepatitis C.
Code History
The ICD-10 code Z11.3 for screening hepatitis C was introduced in October 2015 as part of the regular updates to the ICD-10 coding system. It replaced the previous ICD-9 code V73.89 for the same purpose.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for the ICD-10 code Z11.3 include screening for HCV (hepatitis C virus), testing for hepatitis C, and hepatitis C screening test. These terms can be used interchangeably when documenting patient encounters.
Clinical Information
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver. It is transmitted through blood-to-blood contact, often through sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia. Screening for hepatitis C is important to detect the infection early and prevent complications such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Causes
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The virus is primarily spread through contact with the blood of an infected person. This can occur through sharing needles, receiving a blood transfusion from an infected donor, or from mother to baby during childbirth.
Symptoms
Many people with hepatitis C do not experience any symptoms, especially in the early stages of the infection. However, some common symptoms of hepatitis C include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hepatitis C involves a blood test to detect the presence of HCV antibodies. If the screening test is positive, further tests may be done to determine the level of liver damage and the best course of treatment.
Treatment
Treatment for hepatitis C often involves antiviral medications to help the body clear the virus. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary for advanced liver disease caused by hepatitis C. Early detection through screening is key to successful treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
Screening for hepatitis C is an important preventive measure to detect and treat the infection early. The ICD-10 code Z11.3 is used for documenting screening tests for hepatitis C and is essential for proper billing and tracking of patient encounters.
FAQs
1. Can I use the ICD-10 code Z11.3 for screening hepatitis C in all healthcare settings?
2. What are the risk factors for contracting hepatitis C?
3. Is screening for hepatitis C recommended for everyone?
4. How often should individuals at risk for hepatitis C get screened?
5. Are there any specific guidelines for interpreting screening test results for hepatitis C?