Coding Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation In ICD-10: Understanding The Diagnosis
What is Paroxysmal AF ICD 10?
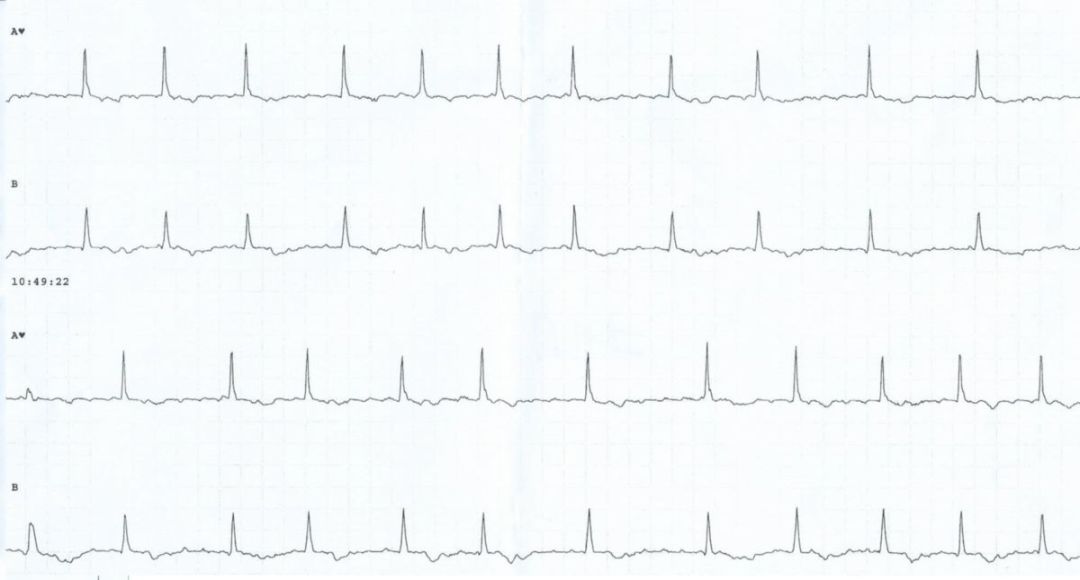
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) is a type of irregular heart rhythm that comes and goes. It is classified under ICD-10 code I48.0 and is characterized by episodes of rapid, chaotic heartbeats that can cause symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
ICD Code History
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a system used by healthcare providers to classify and code diagnoses and procedures. The ICD-10 code for paroxysmal AF was introduced in 1994 and has since been used to classify and track cases of this condition.
Synonyms

Intermittent atrial fibrillation
Episodic atrial fibrillation
Clinical Information
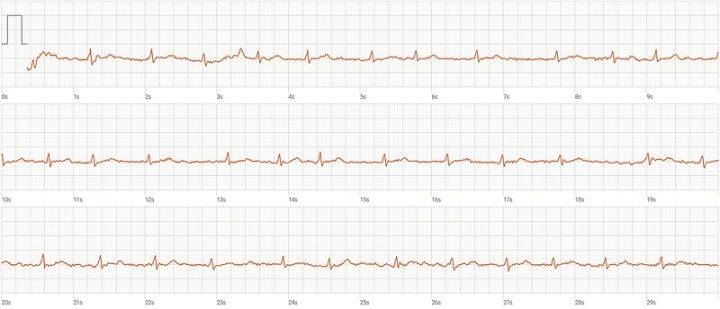
Paroxysmal AF is a common type of AF that typically occurs in episodes lasting for minutes to days. It can be triggered by various factors such as stress, caffeine, alcohol, and certain medications. The condition is associated with an increased risk of stroke and other heart-related complications.
Causes

The exact cause of paroxysmal AF is not fully understood, but factors such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and sleep apnea can increase the risk of developing the condition. Genetics and age also play a role in the development of paroxysmal AF.
Symptoms
Palpitations
Dizziness
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Diagnosis
Diagnosing paroxysmal AF usually involves a physical exam, review of medical history, and tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and Holter monitor to detect irregular heart rhythms. Blood tests may also be done to check for underlying conditions.
Treatment
Treatment for paroxysmal AF aims to control symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of stroke. Options may include medications to regulate heart rhythm and rate, procedures such as cardioversion and catheter ablation, and lifestyle changes such as exercise, healthy diet, and stress management.
Conclusion
Paroxysmal AF is a manageable condition that requires ongoing monitoring and treatment to maintain heart health and quality of life. With proper care and lifestyle modifications, individuals with paroxysmal AF can lead active and fulfilling lives.