A Closer Look At Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: ICD-10 Codes And Diagnosis
What is Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma ICD 10?
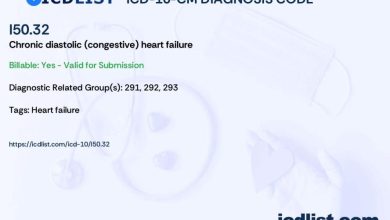
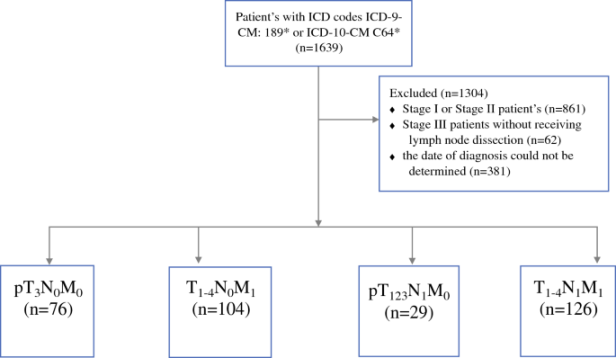
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is a type of kidney cancer that has spread beyond the original site in the kidney to other parts of the body. In the ICD 10 coding system, metastatic renal cell carcinoma is classified as C64.9.
Code Information

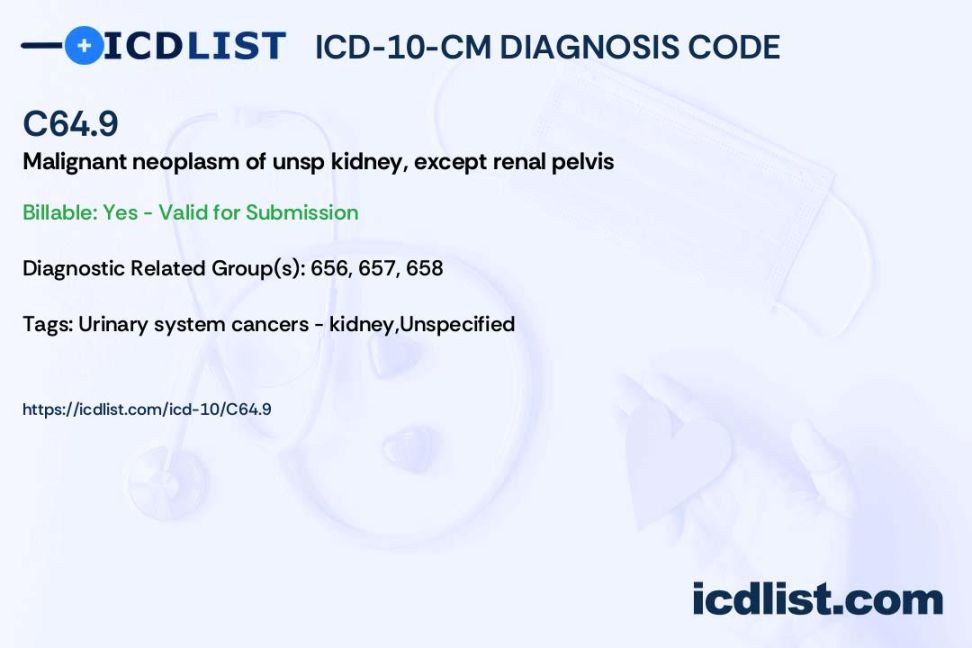
ICD-10-CM Code for Metastatic renal cell carcinoma C64.9
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

MS-DRG Group #717-719 – Other Kidney and Urinary Tract Diagnoses with MCC, with CC, without CC/MCC.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma is 189.0.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma was introduced in October 2015 as part of the larger update to the ICD-10 coding system.
Approximate Synonyms
– Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
– Metastatic RCC
– Metastatic Kidney Cancer
Clinical Information
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer, accounting for about 90% of cases. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma occurs when the cancer cells spread beyond the kidney to other organs such as the lungs, bones, or brain.
Causes
The exact cause of renal cell carcinoma is unknown, but certain risk factors such as smoking, obesity, and high blood pressure may increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Genetic factors may also play a role in some cases.
Symptoms
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma may not cause any symptoms in the early stages. However, as the cancer progresses, symptoms may include blood in the urine, back pain, weight loss, fatigue, and swelling in the legs or abdomen.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma may involve imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans to assess the extent of the cancer spread. A biopsy may also be performed to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment
Treatment options for metastatic renal cell carcinoma may include surgery to remove the primary tumor and affected organs, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. The choice of treatment will depend on the stage of the cancer and the overall health of the patient.
Conclusion
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Patients with this disease should work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their individual needs and goals.
FAQs
1. What is the ICD-10 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
The ICD-10 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma is C64.9.
2. What are the common symptoms of metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Common symptoms of metastatic renal cell carcinoma include blood in the urine, back pain, weight loss, fatigue, and swelling in the legs or abdomen.
3. How is metastatic renal cell carcinoma diagnosed?
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is diagnosed through imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans, and a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
4. What are the treatment options for metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Treatment options may include surgery, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health.
5. What is the prognosis for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
The prognosis for metastatic renal cell carcinoma depends on the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the response to treatment, and the overall health of the patient. Early detection and treatment can improve the chances of a successful outcome.