Adenocarcinoma Of Esophagus: Understanding The ICD-10 Code
What is Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus ICD 10?
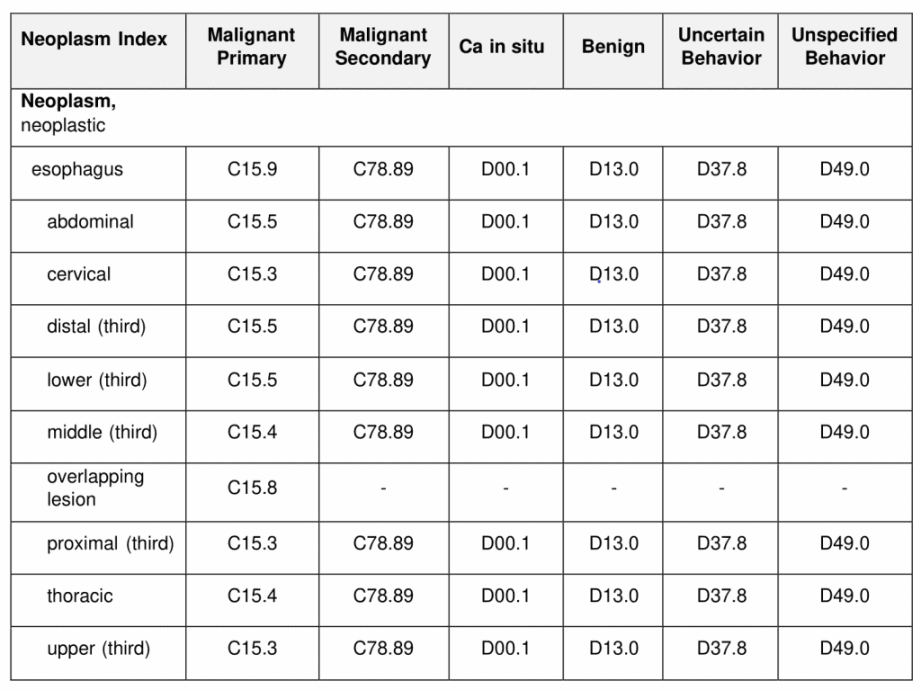
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the esophageal lining. The esophagus is the tube that connects the throat to the stomach, and adenocarcinoma is the most common type of esophageal cancer in the United States. The ICD-10 code for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is C15.5.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is used by healthcare providers to classify and code diagnoses in a standardized way for billing and statistical purposes. This code helps to accurately identify and track cases of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus in healthcare databases.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is classified under MS-DRG 193 – Simple Pneumonia and Pleurisy with MCC. This DRG categorizes patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus who have significant complications or comorbidities that affect their care and treatment.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
In the ICD-9 coding system, adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is classified under code 150.0. Healthcare providers may need to convert this code to the corresponding ICD-10 code (C15.5) when submitting claims for reimbursement or reporting diagnoses.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (C15.5) was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from the ICD-9 coding system to the more advanced ICD-10 system. This change allowed for more detailed and specific coding of diseases and conditions, including adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used interchangeably with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus include esophageal adenocarcinoma and esophageal cancer. These synonyms can help healthcare providers and researchers accurately identify and document cases of this type of cancer.
Clinical Information
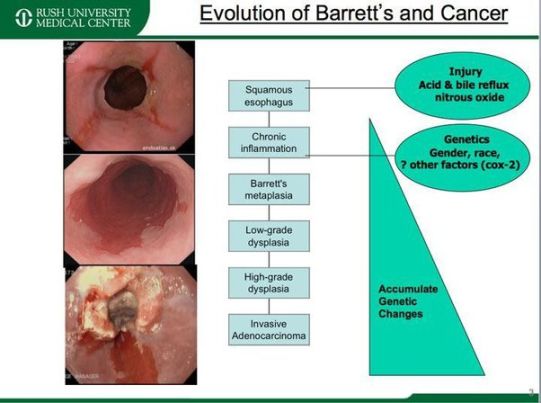
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus typically develops in the lower portion of the esophagus near the stomach. Risk factors for this type of cancer include gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), obesity, smoking, and a diet high in processed meats and low in fruits and vegetables.
Causes
The exact cause of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is unknown, but it is believed to be related to chronic irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining. This can lead to changes in the cells of the esophagus that eventually become cancerous.
Symptoms

Common symptoms of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus include difficulty swallowing, unintentional weight loss, chest pain or discomfort, and persistent indigestion or heartburn. These symptoms may worsen over time as the cancer grows and spreads.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing adenocarcinoma of the esophagus typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as a barium swallow or CT scan, and a biopsy of the esophageal tissue. Once a diagnosis is confirmed, healthcare providers will determine the stage of the cancer to guide treatment decisions.
Treatment
Treatment for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus may include surgery to remove the cancerous tissue, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy to target and kill cancer cells, and palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The specific treatment plan will depend on the stage and location of the cancer.
Conclusion
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus is a serious and potentially life-threatening type of cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers use the ICD-10 code C15.5 to accurately classify and document cases of this cancer for billing and statistical purposes. Early detection and intervention can improve outcomes and quality of life for patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus?
Risk factors for adenocarcinoma of the