Exploring The ICD-10 Codes For Carotid Vascular Disease
What is Carotid Vascular Disease ICD 10?
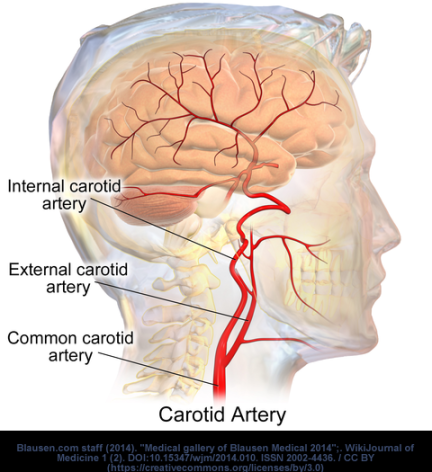
Carotid vascular disease ICD 10 refers to a group of health conditions that affect the carotid arteries, which are the main blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. These conditions can include atherosclerosis, carotid artery stenosis, and other vascular disorders that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for carotid vascular disease is I65.2. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to carotid artery stenosis, atherosclerosis of the carotid artery, and other vascular disorders affecting the carotid arteries.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Carotid vascular disease falls under MS-DRG 299, which includes cases of carotid artery stenosis and other vascular disorders of the head and neck. This DRG is used to classify and reimburse healthcare providers for the treatment of patients with these conditions.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
In the ICD-9 coding system, carotid vascular disease is classified under code 433.10. This code is used to indicate atherosclerosis of the carotid artery without mention of cerebral infarction.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for carotid vascular disease was introduced in October 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems. This new code provided more specific and detailed classification for carotid artery disorders.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for carotid vascular disease include carotid artery stenosis, carotid artery atherosclerosis, and carotid artery occlusion. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe conditions affecting the carotid arteries.
Clinical Information
Carotid vascular disease can lead to serious health complications, including stroke, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), and other neurological deficits. It is important to diagnose and treat these conditions early to prevent further complications and improve patient outcomes.
Causes
The main cause of carotid vascular disease is atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the carotid arteries. This can lead to narrowing of the arteries, reduced blood flow to the brain, and an increased risk of blood clots and stroke.
Symptoms
Symptoms of carotid vascular disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms may include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, dizziness, and headaches.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of carotid vascular disease typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests such as carotid ultrasound or angiography, and blood tests to assess cholesterol levels and other risk factors. A healthcare provider may also perform a neurological exam to evaluate any neurological deficits.
Treatment
Treatment for carotid vascular disease may include lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, medications to control cholesterol and blood pressure, and surgical interventions such as carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty with stenting. The goal of treatment is to reduce the risk of stroke and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Carotid vascular disease is a serious health condition that can lead to stroke and other complications if left untreated. It is important to diagnose and treat these conditions early to prevent further damage to the carotid arteries and improve patient outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for carotid vascular disease?
Common risk factors for carotid vascular disease include smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of cardiovascular disease.
2. Can carotid vascular disease be prevented?
Yes, carotid vascular disease can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, controlling risk factors such as high cholesterol and blood pressure, and seeking regular medical check-ups.
3. How is carotid vascular disease diagnosed?
Carotid vascular disease is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, blood tests, and neurological evaluation by a healthcare provider.