Understanding Crohn’s Disease: ICD-10 Coding And Diagnosis
What is Crohn’s Disease ICD-10?
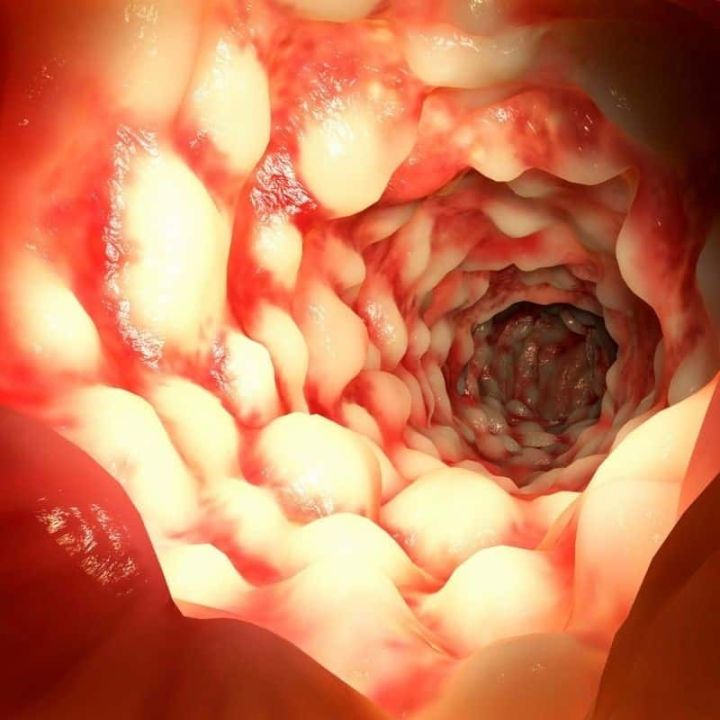
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It is characterized by inflammation and ulceration of the lining of the intestines, which can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications. Crohn’s disease is classified under the ICD-10 code K50.
Code Information

The ICD-10 code for Crohn’s disease is K50. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to Crohn’s disease in medical records and billing systems. It provides a standardized way to document and track cases of Crohn’s disease for statistical and research purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

Crohn’s disease is categorized under the MS-DRG 330, which includes gastrointestinal infections and inflammations with complications. This DRG is used to group together similar medical cases for billing and reimbursement purposes in healthcare settings.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The equivalent ICD-9 code for Crohn’s disease is 555, which falls under the category of regional enteritis. This code was used prior to the implementation of the ICD-10 coding system and is still sometimes referenced in older medical records.
Code History

The ICD-10 code K50 for Crohn’s disease was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from the ICD-9 coding system. It replaced the previous code for Crohn’s disease in order to provide a more detailed and specific classification for this condition.
Approximate Synonyms
Granulomatous colitis
Ileocolitis
Regional enteritis
Terminal ileitis
Clinical Information
Crohn’s disease is a complex condition that involves inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract. It can cause a wide range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and malnutrition. In severe cases, Crohn’s disease can lead to complications such as bowel obstructions, fistulas, and abscesses.
Causes
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors. People with a family history of the disease are at a higher risk of developing it, as are individuals who smoke or have a compromised immune system.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Crohn’s disease include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and blood in the stool. Some people may also experience fever, nausea, vomiting, and joint pain. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. A colonoscopy or endoscopy may be performed to visualize the intestines and take tissue samples for biopsy. Blood tests can also help to assess inflammation levels and nutritional deficiencies.
Treatment
Treatment for Crohn’s disease aims to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent complications. This may involve medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologic therapies. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove diseased portions of the intestines or repair complications such as fistulas or strictures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that can cause a variety of symptoms and complications. It is classified under the ICD-10 code K50 and is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Treatment options include medication and surgery to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
FAQs
Can Crohn’s disease be cured?
There is currently no cure for Crohn’s disease, but treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Is Crohn’s disease hereditary?
While genetics play a role in the development of Crohn’s disease, it is not entirely hereditary. Having a family history of the disease can increase your risk, but other factors also contribute.
Can diet affect Crohn’s disease?
Diet can play a role in managing