Understanding Stage 4 Lung Cancer: ICD-10 Codes And Diagnosis
What is Stage 4 Lung Cancer ICD 10?
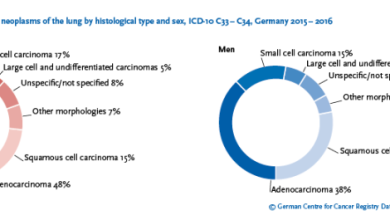
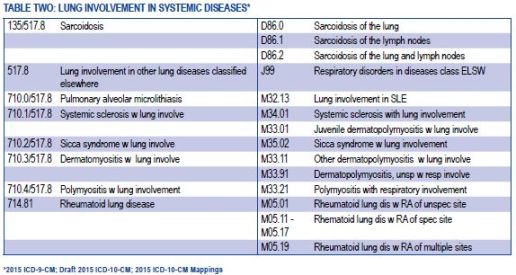
Stage 4 lung cancer is the most advanced stage of lung cancer, where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the lungs. The ICD-10 code for stage 4 lung cancer is C34.9. This stage of cancer is often considered incurable, but treatments are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Code Information
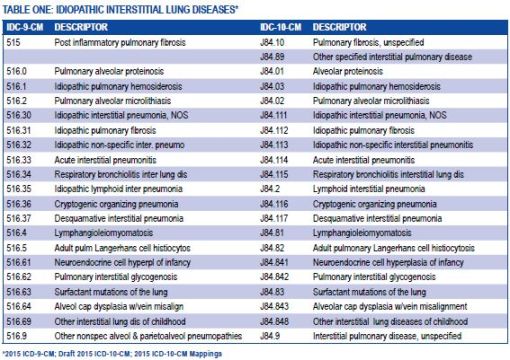
The ICD-10 code for stage 4 lung cancer is C34.9. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses of lung cancer in medical records and billing purposes. It helps healthcare providers and insurance companies categorize the disease for proper treatment and reimbursement.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
For stage 4 lung cancer, the MS-DRG code is 793. This code is used for Medicare reimbursement purposes to classify patients with stage 4 lung cancer for inpatient hospital stays.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

To convert the ICD-10 code C34.9 for stage 4 lung cancer to ICD-9 code, it would be 162.9. The ICD-9 code is an older coding system that was used before the implementation of ICD-10.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for stage 4 lung cancer was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding system. This transition was made to modernize and improve the accuracy of medical coding and billing processes.
Approximate Synonyms
Some approximate synonyms for stage 4 lung cancer include metastatic lung cancer, advanced lung cancer, and late-stage lung cancer. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the same advanced stage of the disease.
Clinical Information
Stage 4 lung cancer is characterized by the spread of cancer cells from the lungs to other parts of the body, such as the liver, bones, or brain. Symptoms may include persistent cough, chest pain, weight loss, and difficulty breathing. Treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care.
Causes
The primary cause of lung cancer, including stage 4 lung cancer, is smoking. However, non-smokers can also develop lung cancer due to exposure to secondhand smoke, radon gas, asbestos, and other environmental factors. Genetic factors may also play a role in the development of lung cancer.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of stage 4 lung cancer include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing, hoarseness, weight loss, fatigue, and recurrent respiratory infections. Advanced stage symptoms may also include bone pain, headaches, confusion, and jaundice.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing stage 4 lung cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as CT scans, PET scans, and MRI scans, as well as biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells. Blood tests may also be performed to assess the level of tumor markers in the blood.
Treatment
Treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care. The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, control the spread of cancer, and improve quality of life. Clinical trials may also be available for patients to explore new treatment options.
Conclusion
Stage 4 lung cancer is a serious and advanced stage of the disease, where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes and quality of life for patients with stage 4 lung cancer. It is important for individuals at risk of lung cancer to quit smoking, avoid exposure to harmful substances, and seek regular medical screenings for early detection.
FAQs
1. Can stage 4 lung cancer be cured?
Stage 4 lung cancer is often considered incurable, but treatments are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
2. What are the survival rates for stage 4 lung cancer?
The survival rates for stage 4 lung cancer vary depending on the individual’s overall health, response to treatment, and other factors. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized prognosis and treatment options.
3