Giant Cell Tumor Of Tendon Sheath: Understanding The ICD-10 Code
What is Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath ICD 10?
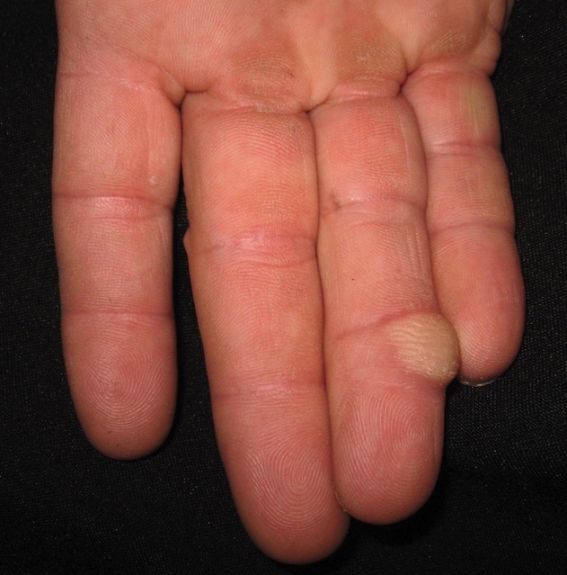
Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath (GCTTS), also known as localized nodular tenosynovitis, is a benign tumor that commonly occurs in the hands and fingers, although it can also be found in other parts of the body such as the feet, ankles, and knees. It is characterized by the presence of giant cells within the synovial lining of the tendon sheath.
The ICD-10 code for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is M67.1. This code is used to classify and report medical conditions for billing and statistical purposes.
Code Information
ICD-10 Code: M67.1
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
There is no specific MS-DRG related to Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath as it is a benign condition that does not typically require inpatient treatment.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The equivalent ICD-9 code for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is 727.7.
Code History
The ICD-10 code M67.1 for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath was implemented on October 1, 2015, as part of the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems.
Approximate Synonyms

Other terms that may be used interchangeably with Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath include localized nodular tenosynovitis and pigmented villonodular synovitis.
Clinical Information
Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is a rare condition that is more commonly seen in adults between the ages of 30 and 50, although it can occur at any age. It is typically slow-growing and non-metastasizing, meaning it does not spread to other parts of the body.
Causes
The exact cause of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is unknown, but it is believed to be related to inflammation or trauma to the tendon sheath. It may also be associated with certain genetic factors.
Symptoms
Patients with Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath may experience pain, swelling, and limited range of motion in the affected joint. In some cases, a palpable mass may be present.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is typically made based on clinical examination, imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI, and biopsy of the lesion to confirm the presence of giant cells.
Treatment
Treatment for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath may include observation, corticosteroid injections, surgical excision of the tumor, or radiation therapy in cases of recurrence or aggressive growth.
Conclusion
Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is a benign condition that most commonly affects the hands and fingers. While it is typically slow-growing and non-metastasizing, it can cause pain and limited mobility in the affected joint. Diagnosis is made through clinical examination, imaging studies, and biopsy, with treatment options including observation, corticosteroid injections, surgery, and radiation therapy. Early detection and intervention are key to successful management of this condition.
FAQs
Can Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath recur after treatment?
Yes, Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath can recur in some cases, requiring further treatment.
Is Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath a cancerous condition?
No, Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is a benign tumor and is not considered cancerous.
Who is at risk for developing Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath?
Adults between the ages of 30 and 50 are more commonly affected by this condition, although it can occur at any age.
What are the treatment options for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath?
Treatment may include observation, corticosteroid injections, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Can Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath cause permanent damage?
In some cases, Giant Cell T