Understanding The Coding For Aortic Root Dilation In ICD-10
What is ICD-10 code for Aortic Root Dilation?
The ICD-10 code for Aortic Root Dilation is I28.2. This code is used to classify and track cases of aortic root dilation in medical records for billing and statistical purposes.
Code Information
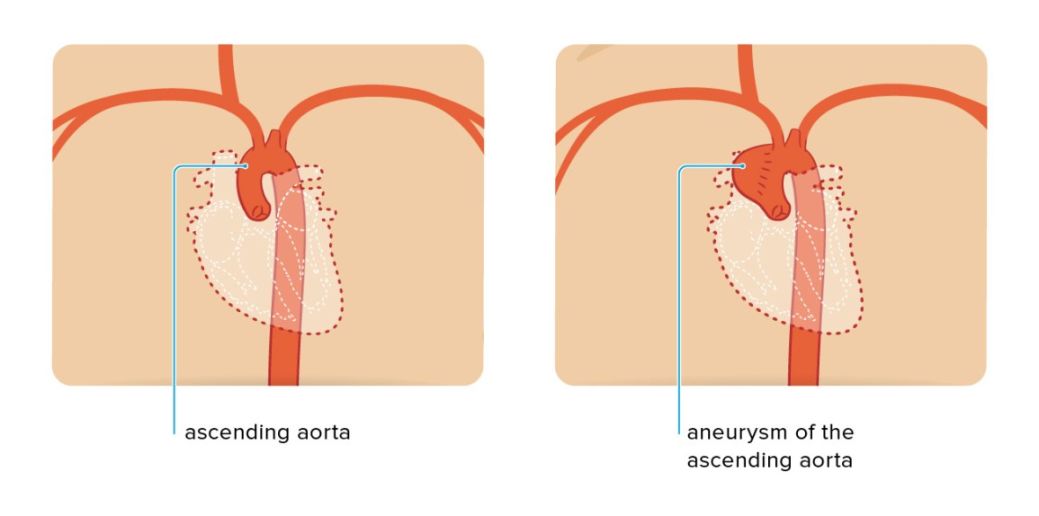
The ICD-10 code I28.2 specifically refers to Aneurysm of aorta, unspecified site. This code is used to document cases of aortic root dilation in medical records and is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Patients with aortic root dilation may be classified under MS-DRG 314 – Other Circulatory System Diagnoses with MCC (Major Complications or Comorbidities). This DRG is used to group patients with similar diagnoses for billing and reimbursement purposes.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
The ICD-9 code equivalent to ICD-10 code I28.2 for Aortic Root Dilation is 441.4 – Aortic aneurysm of unspecified site. This code was used prior to the implementation of ICD-10 and may still be referenced in some medical records.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for Aortic Root Dilation was introduced as part of the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision in 2015. It replaced the previous ICD-9 code 441.4 and provided a more specific classification for cases of aortic root dilation.
Approximate Synonyms
Dilation of aortic root
Aortic root aneurysm
Aortic root enlargement
Clinical Information
Aortic root dilation is a condition characterized by the abnormal widening or bulging of the aortic root, which is the section of the aorta closest to the heart. This can lead to complications such as aortic dissection or rupture if left untreated.
Causes
Aortic root dilation can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, connective tissue disorders, high blood pressure, and atherosclerosis. In some cases, it may be associated with underlying heart conditions or congenital abnormalities.
Symptoms
Patients with aortic root dilation may experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue. In severe cases, there may be signs of aortic dissection or rupture, which require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of aortic root dilation typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests such as echocardiography or CT scans, and genetic testing in some cases. The size and extent of the dilation will determine the appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment
Treatment for aortic root dilation may include medication to control blood pressure and heart rate, lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors, and surgical intervention in severe cases. Options such as aortic root replacement or repair may be considered to prevent complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Aortic Root Dilation is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications such as aortic dissection or rupture. Proper coding using the ICD-10 code I28.2 is essential for accurate documentation and tracking of cases in medical records.
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for developing Aortic Root Dilation?
Factors such as genetics, high blood pressure, and connective tissue disorders can increase the risk of developing aortic root dilation.
2. How is Aortic Root Dilation diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as echocardiography and CT scans, as well as genetic testing in some cases.
3. What are the treatment options for Aortic Root Dilation?
Treatment may include medication, lifestyle changes, and surgical intervention such as aortic root replacement or repair.
4. Can Aortic Root Dilation be prevented?
While some risk factors such as genetics cannot be changed, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of developing aortic root dilation.
5. What should I do if I suspect I have Aortic Root Dilation?
If you experience symptoms such