Allergic Asthma Coding: Understanding The ICD-10 Guidelines
What is Allergic Asthma?
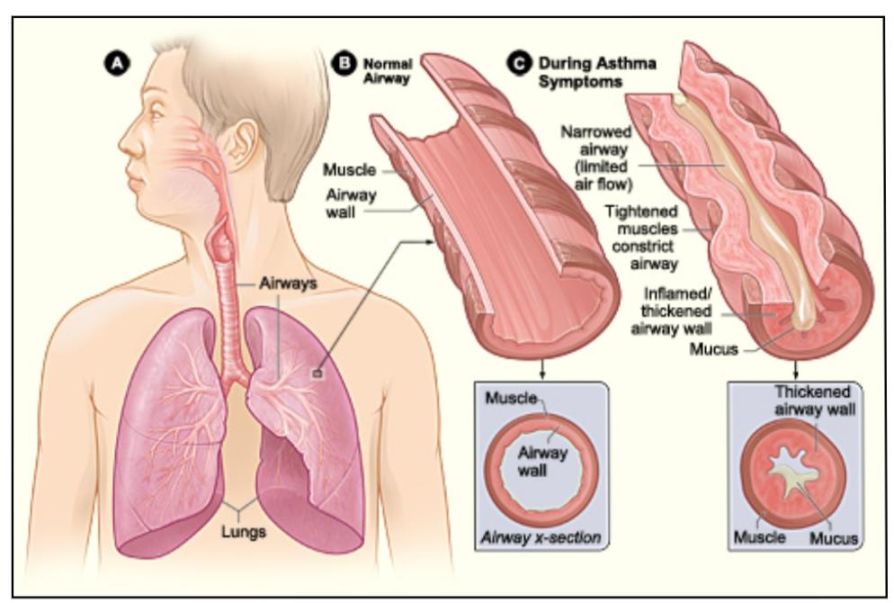
Allergic asthma is a type of asthma that is triggered by exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. When a person with allergic asthma is exposed to these triggers, their immune system reacts by causing inflammation in the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for allergic asthma is J45.909. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses of allergic asthma in medical records and for billing purposes.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)

For allergic asthma, the MS-DRG is 202 – Bronchitis and Asthma with CC/MCC. This DRG is used to classify patients with allergic asthma who require hospitalization and treatment.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The ICD-9 code equivalent to J45.909 is 493.90 – Asthma, unspecified type, unspecified.
Code History

The ICD-10 code for allergic asthma was introduced in 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems. It replaced the previous code for allergic asthma, which was J45.901.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that can be used to describe allergic asthma include atopic asthma, extrinsic asthma, and allergic bronchial asthma.
Clinical Information
Allergic asthma is a common type of asthma that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation of the airways and increased mucus production in response to allergen exposure.
Causes
Allergic asthma is caused by an overreaction of the immune system to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. When a person with allergic asthma is exposed to these triggers, their immune system releases chemicals that cause inflammation in the airways.
Symptoms
The symptoms of allergic asthma can vary from person to person but commonly include wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may be triggered by specific allergens.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing allergic asthma involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, lung function tests, and allergy testing. A doctor may also recommend imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans to rule out other possible causes of symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment for allergic asthma typically involves a combination of medications such as inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and allergy medications. In some cases, allergen immunotherapy or biologic therapies may be recommended to help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of asthma attacks.
Conclusion
Allergic asthma is a common type of asthma that is triggered by exposure to allergens. It is important for individuals with allergic asthma to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for allergic asthma, individuals can take steps to improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of this chronic condition.
FAQs
1. What are the common triggers for allergic asthma?
The common triggers for allergic asthma include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold.
2. Can allergic asthma be cured?
Allergic asthma cannot be cured, but it can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes.
3. Are there any natural remedies for allergic asthma?
Some natural remedies such as breathing exercises, herbal supplements, and essential oils may help with symptom management, but it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new treatments.
4. Is there a genetic component to allergic asthma?
Yes, allergic asthma can run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition.
5. How can I prevent asthma attacks related to allergies?
To prevent asthma attacks related to allergies, it is important to identify and avoid triggers, take prescribed medications as directed, and follow an asthma action plan provided by a healthcare provider.