Understanding The Severity Of Stage 4 Lung Cancer In ICD-10 Coding
What is ICD 10 Stage 4 Lung Cancer?
ICD 10 Stage 4 Lung Cancer is a diagnostic code used to classify advanced stage lung cancer in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) system. Stage 4 lung cancer is the most advanced stage of the disease, where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the lungs.
Code Information
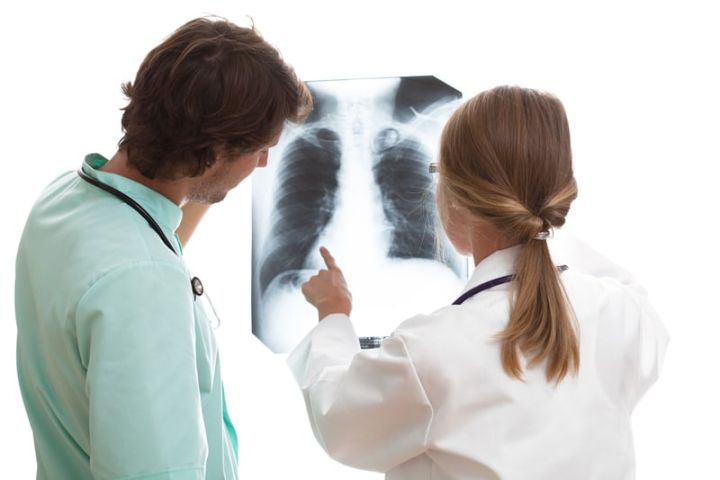
The ICD 10 code for stage 4 lung cancer is C34.9, which falls under the category of malignant neoplasms of the bronchus and lung. This code is used by healthcare providers to accurately diagnose and track the progression of the disease.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
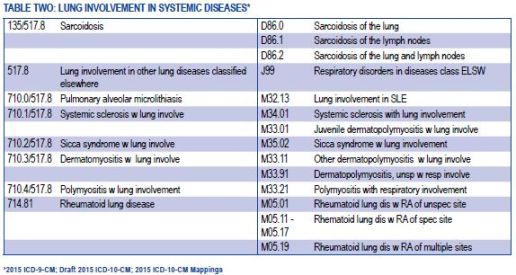
In the Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Group (MS-DRG) system, stage 4 lung cancer is classified under DRG 165 – Major Thoracic and Abdominal Procedures for Neoplastic Disease with MCC (Major Complications and Comorbidities). This grouping helps determine the reimbursement rates for treating patients with stage 4 lung cancer.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
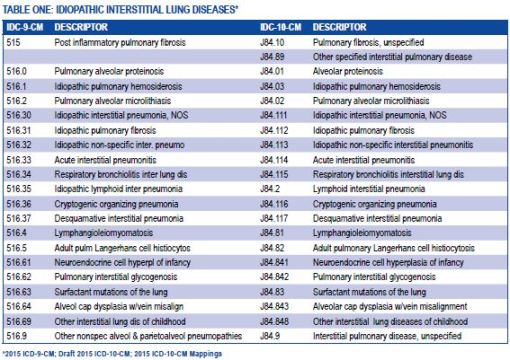
For those still using the ICD-9 coding system, the equivalent code for ICD 10 Stage 4 Lung Cancer is 162.9, which is classified under malignant neoplasm of the trachea, bronchus, and lung.
Code History
The ICD 10 code for stage 4 lung cancer was implemented in October 2015 as part of the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems. This change was made to provide more detailed and specific codes for accurate diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, including lung cancer.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms used interchangeably with ICD 10 Stage 4 Lung Cancer include metastatic lung cancer, advanced lung carcinoma, and late-stage lung adenocarcinoma. These synonyms help describe the same condition of advanced stage lung cancer.
Clinical Information
Stage 4 lung cancer is characterized by the spread of cancer cells to distant organs or tissues in the body, such as the brain, bones, liver, or other parts of the lungs. This advanced stage of the disease often presents with severe symptoms and requires aggressive treatment.
Causes
The primary cause of stage 4 lung cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lungs, which can be triggered by genetic mutations, exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke or asbestos, and a family history of lung cancer. Other risk factors include age, gender, and environmental factors.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of stage 4 lung cancer include persistent coughing, chest pain, difficulty breathing, coughing up blood, fatigue, weight loss, and recurring infections. As the cancer spreads to other parts of the body, additional symptoms may manifest depending on the affected organs.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing stage 4 lung cancer involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, imaging tests like CT scans and MRIs, and biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells. Staging helps determine the extent of cancer spread and guides treatment decisions.
Treatment
Treatment for stage 4 lung cancer typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The goal of treatment is to slow the progression of the disease and prolong survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ICD 10 Stage 4 Lung Cancer is a severe and advanced form of lung cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. Healthcare providers use specific diagnostic codes to accurately classify and manage patients with stage 4 lung cancer. Early detection and personalized treatment plans are essential in improving outcomes and patient survival.
FAQs
1. Can stage 4 lung cancer be cured?
Unfortunately, stage 4 lung cancer is considered incurable, but treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
2. What is the prognosis for stage 4 lung cancer?
The prognosis for stage 4 lung cancer is generally poor, with a lower survival rate compared to earlier stages of the disease.
3. What are the risk factors for developing stage 4 lung cancer?
Risk factors for stage 4 lung cancer include smoking, exposure to asbestos or other carcinogens, family history of lung cancer, and genetic mutations.
4. What are the treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer?
Treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care.
5. How can I lower my risk of developing lung cancer?
To lower your risk of developing lung cancer, avoid smoking, limit exposure to carcinogens, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and undergo regular screenings for early detection.