ICD-10 Diagnosis Code For Vaginal Odor: R10.83
What is Vaginal Odor ICD-10?
Vaginal odor ICD-10 is a medical code used to classify and document cases of abnormal or unpleasant vaginal odor. This condition can be indicative of an underlying infection or imbalance in the vaginal flora.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for vaginal odor is N76.0. This code falls under the category of noninflammatory disorders of vagina.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
There is no specific MS-DRG related to vaginal odor as it is not a condition that typically requires hospitalization or surgical intervention.
Convert to ICD-9 Code

The equivalent ICD-9 code for vaginal odor is 616.10 – Vaginitis and vulvovaginitis, unspecified.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for vaginal odor was introduced in 2015 as part of the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems.
Approximate Synonyms
Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Abnormal vaginal odor
Malodorous vagina
Clinical Information
Vaginal odor can be a sign of various conditions such as bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, sexually transmitted infections, or poor hygiene. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
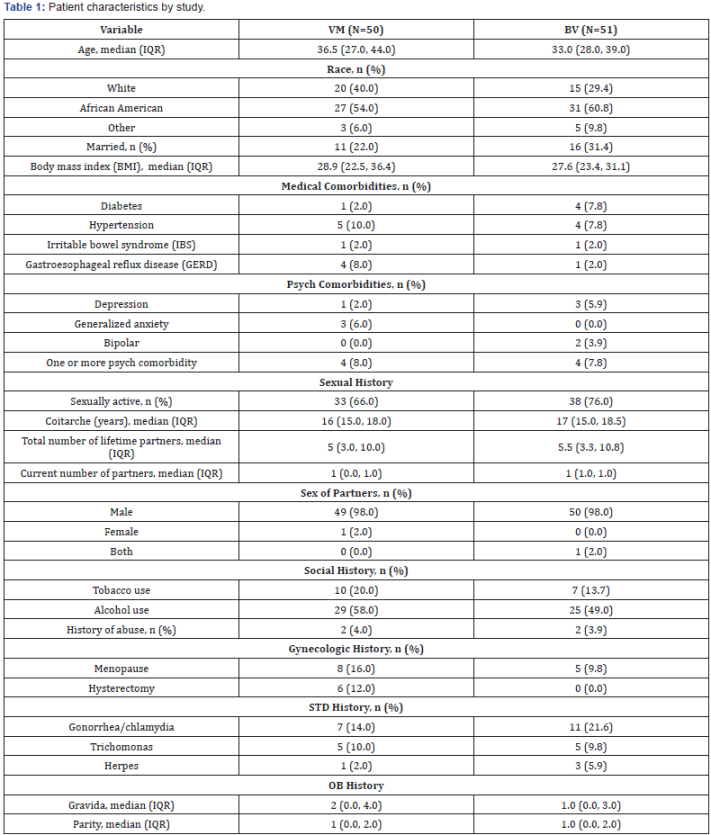
Causes of Vaginal Odor
The most common causes of vaginal odor include bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, poor hygiene practices, hormonal changes, and sexually transmitted infections.
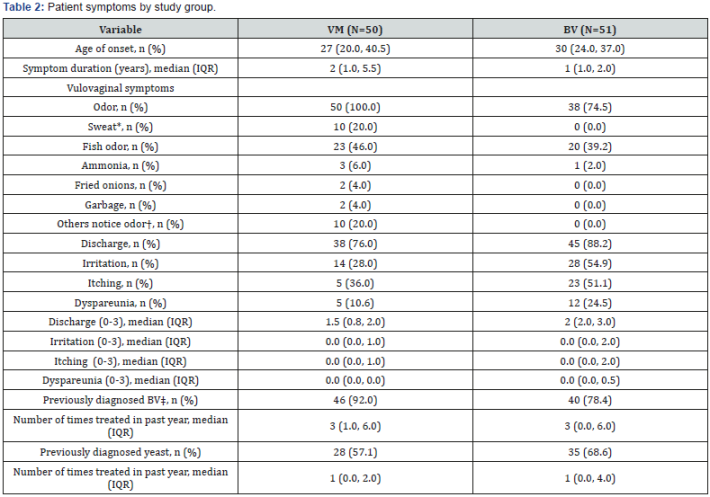
Symptoms of Vaginal Odor
Some common symptoms associated with vaginal odor include a strong, unpleasant smell, abnormal discharge, itching or irritation in the vaginal area, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of vaginal odor typically involves a physical examination, a review of symptoms, and laboratory tests such as vaginal swabs or urine tests to identify the underlying cause of the odor.
Treatment
Treatment for vaginal odor depends on the underlying cause. It may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal medications for yeast infections, or medication for sexually transmitted infections. Maintaining good hygiene practices and avoiding irritants can also help alleviate symptoms.
Conclusion
Vaginal odor is a common issue that can be caused by various factors. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
FAQs
1. Is vaginal odor a sign of a serious medical condition?
2. Can vaginal odor be treated at home with over-the-counter remedies?
3. How can I prevent vaginal odor?
4. When should I see a healthcare provider for vaginal odor?
5. Are there any natural remedies for vaginal odor?